Figure 1.
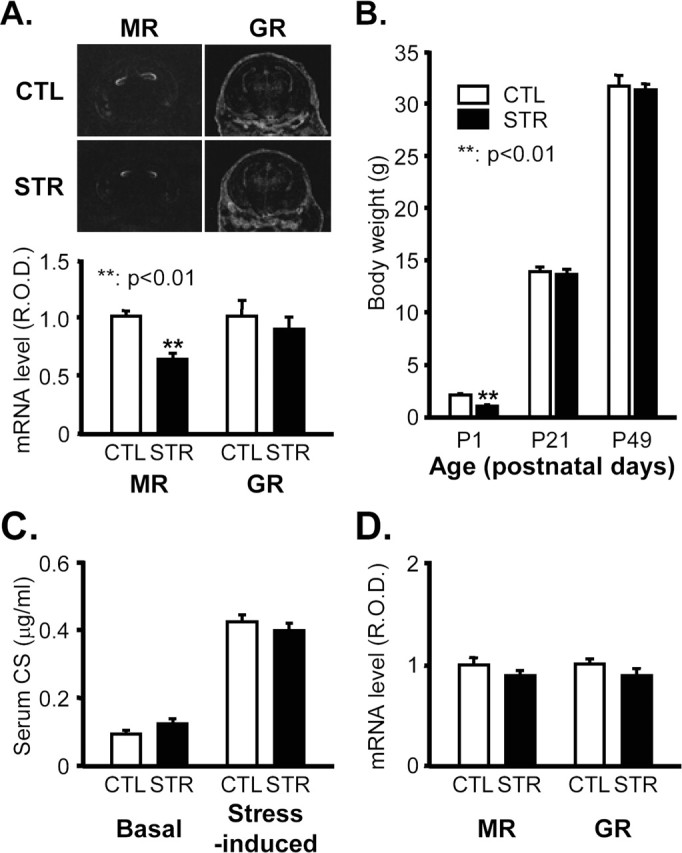
Physiological parameters of maternally stressed mice. A, MR and GR mRNA levels 18.5 dpc in the developing hippocampus of CTL and STR mice determined by in situ hybridization. Top panel shows representative photographs of in situ hybridizations. R.O.D. of hybridization signals in the hippocampal regions were quantified with Bio1D image analysis software and are represented an arbitrary units in the bottom panel (**p < 0.01; n = 6 for each group). B, Body weights of mice at the age of P1, P21 (3-week-old), and P49 (7-week-old) (means ± SEM). **p < 0.01 versus CTL; n = 174 for P1 CTL mice per group; n = 157 for P1 STR mice per group; n = 28 for P21 mice per group; n = 28 for P49 mice per group. C, Basal and stress-induced levels of serum CS in 7-week-old adult offspring expressed as means ± SEM (n = 10 for each group). The stress-evoked increase in serum CS was measured in mice that received 30 min of immobilization stress. D, MR and GR mRNA levels in the hippocampus of 7-week-old adult offspring determined by in situ hybridization. R.O.D. are presented in arbitrary units (n = 5 for each group).
