Figure 9.
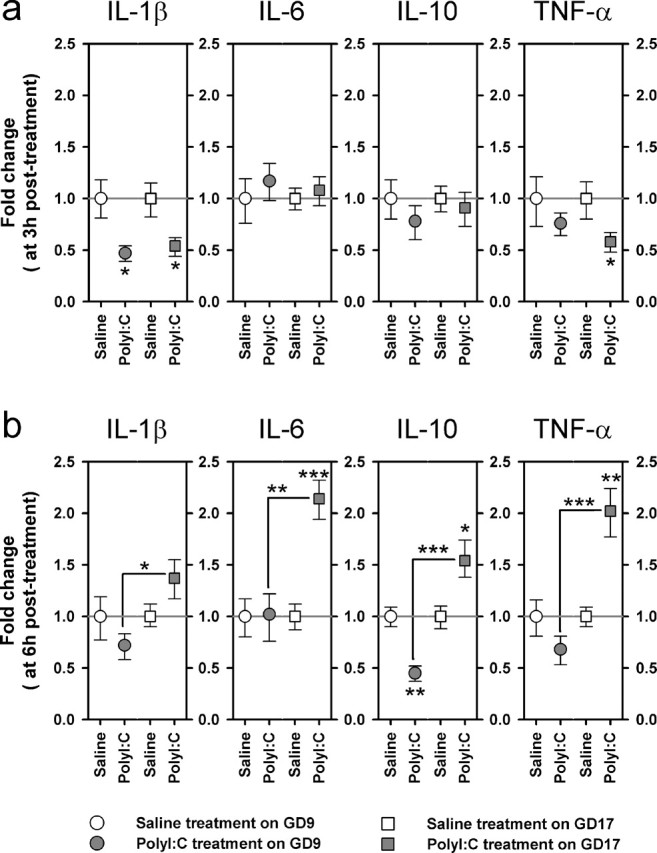
Comparison of the fetal brain cytokine responses after immune challenge in middle and late gestation in terms of relative gene expression levels. The graphs illustrate the fold changes in the relative cytokine gene expression as calculated using the 2-ΔΔCt method; the bars correspond to the minus and plus range of the fold changes. At each sample interval (3 and 6 h), the average fetal brain cytokine levels obtained per progeny (n = 3–4 fetuses per progeny) was submitted to statistical analyses. a, At 3 h after treatment, the relative gene expression levels of IL-1β were reduced in the fetal brains as a result of maternal PolyI:C exposure in both gestation day conditions, whereas a similar reduction in TNF-α expression was only observed in the brains of fetuses derived from immune-challenged GD17 dams. The relative expression levels of IL-6 and IL-10 genes were unaffected by the maternal treatment at this sampling time. b, At 6 h after treatment, maternal immune stimulation on GD17 significantly increased the relative gene expression levels of IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α, whereas the same treatment conducted on GD9 exerted an opposite effect on the relative IL-10 gene expression levels. The number of pregnant dams in each group was 4, except in the following three groups: GD9-PolyI:C/3 h, n = 6; GD17-PolyI:C/3 h, n = 5; GD17-PolyI:C/6 h, n = 5. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001, statistical significance based on independent Student's t tests between the effects of PolyI:C treatment on GD9 (GD9-PolyI:C vs GD9-saline) and on GD17 (GD17-PolyI:C vs GD17-saline), as well as between the efficacy of PolyI:C treatment at the two treatment days (GD9-PolyI:C vs GD17-PolyI:C) at each sample interval (3 or 6 h).
