Figure 5.
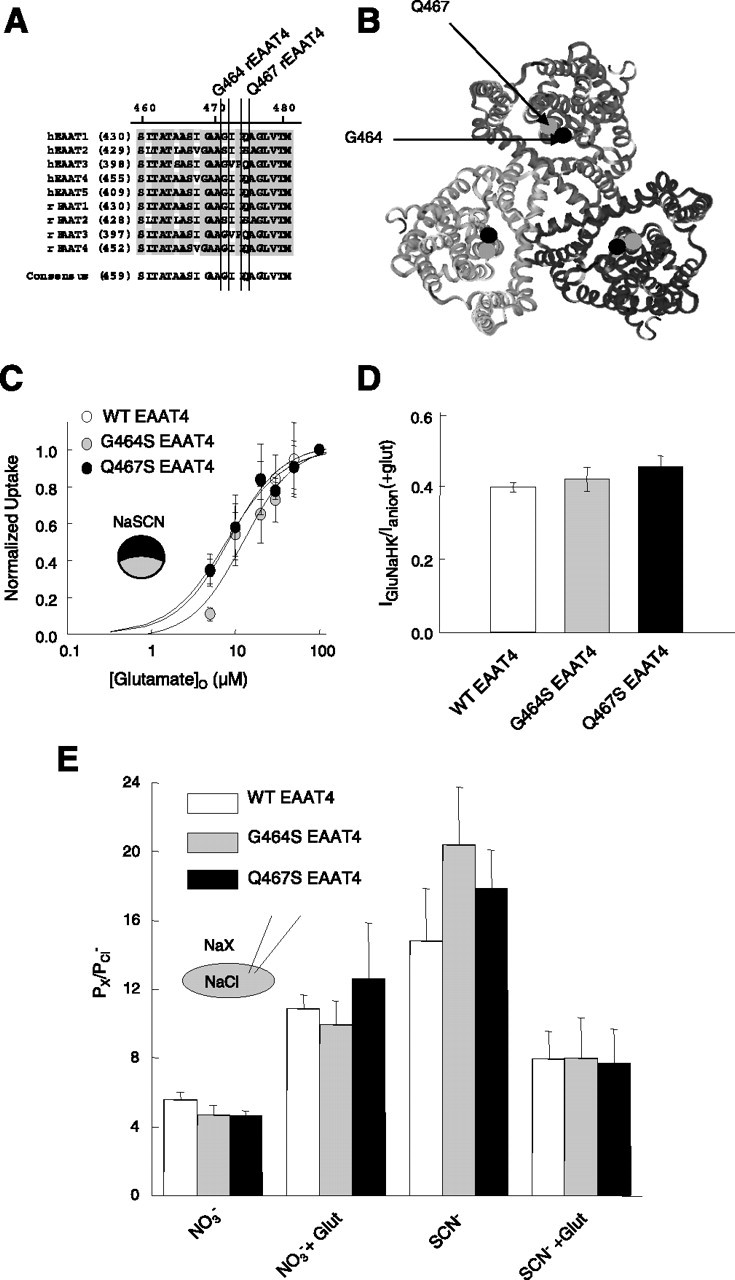
Effects of two point mutations close to the putative glutamate binding site on coupled and uncoupled transport. A, Alignment of the region containing G464 and Q467 in various human and rat EAAT isoforms. B, Localization of the residues corresponding to G464 (black) and Q467 (gray) of EAAT4 in the ribbon presentation of the three-dimensional structure of the P. horikoshii glutamate transporter (Yernool et al., 2004), viewed from the external membrane site. C, Glutamate dependence of radioactive glutamate uptake by WT and mutant EAAT4. Means ± SEM from eight cells for each glutamate concentration. D, Ratio of uptake current to anion current amplitudes from at least five cells for WT and mutant EAAT4 transporters at 0.5 mm glutamate. E, Anion permeability ratios for WT and mutant EAAT4 in the presence of 0.5 mm glutamate (Glut) for at least four cells.
