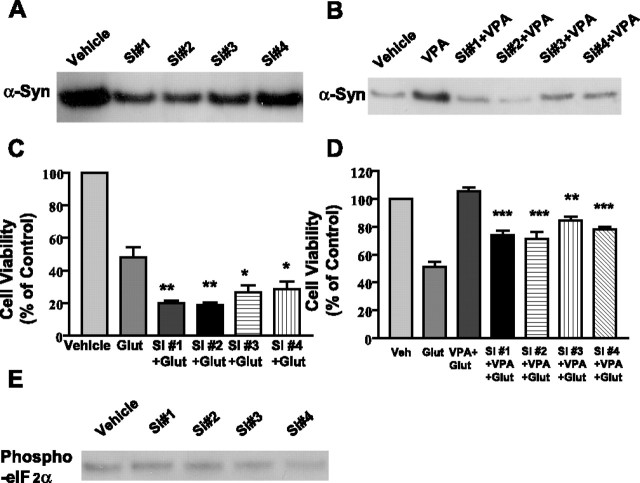
Figure 6.
Individual siRNA decreases basal and VPA-stimulated α-syn protein levels, exacerbates glutamate-induced excitotoxicity, and attenuates VPA neuroprotection. Cells were exposed to 100 nm individual α-syn siRNA (S#1, S#2, S#3, or S#4) for 24 h before pretreatment with vehicle or 0.4 mm VPA for 6 d (DIV 1 to DIV 7). Cells were then harvested for Western blotting of α-syn protein (A, B) or further incubated without or with glutamate (Glut; 100 μm) for 24 h (C, D). Cell viability was quantified by MTT assay from three independent cultures. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01 compared with glutamate group in C. ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001 compared with VPA plus glutamate group in D. Cell lysates from A were also used for immunoblotting of phospho-eIF 2α protein levels (E). Western blots are results from a typical experiment.