Figure 5.
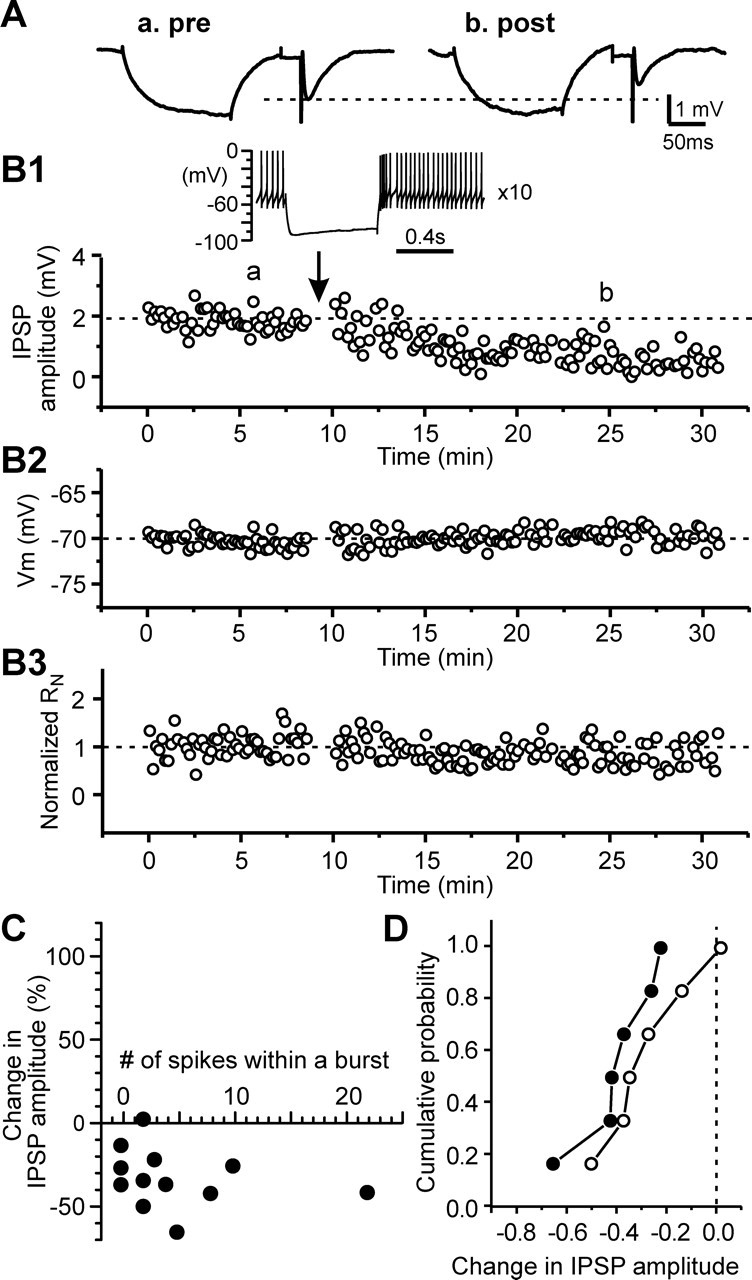
Rebound bursts induce long-lasting depression of IPSPs in the presence of L-type calcium channel blocker. A, Average traces of IPSPs during control (a) and after rebound bursts (b) taken from an STN cell in the presence of 20 μm nimodipine. B, Time courses of IPSP amplitude (B1), membrane potential (B2), and normalized input resistance (B3) during control and after triggering rebound burst 10 times for the cell in A. Inset, A rebound burst triggered by hyperpolarizing current pulse (−250 pA and 600 ms in duration), showing four spikes within a rebound burst. C, Plot of the change in IPSP amplitude and the number of rebound spikes that had interspike intervals shorter than half of those during the base spontaneous activity. D, Cumulative probability histograms for cells with three or more rebound spikes (filled symbols) and those with two or no rebound burst spikes (open symbols). p > 0.5, Kolmogorov–Smirnov test.
