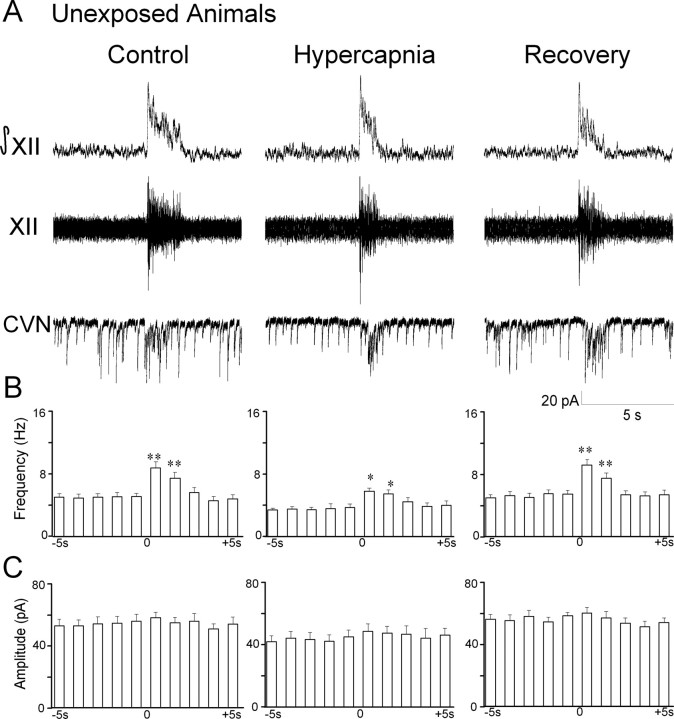
Figure 3.
Hypercapnia diminishes GABAergic IPSC frequency. GABAergic synaptic activity was isolated by focal application of NMDA, non-NMDA, and glycinergic receptor antagonists. A, As shown for a typical experiment, GABAergic IPSC frequency significantly increased during respiratory bursts. B, After exposure to hypercapnia, both spontaneous and inspiratory GABAergic IPSC frequency was depressed. C, GABAergic IPSC amplitude was not modulated by respiratory bursts; however, hypercapnia diminished IPSC amplitude. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.