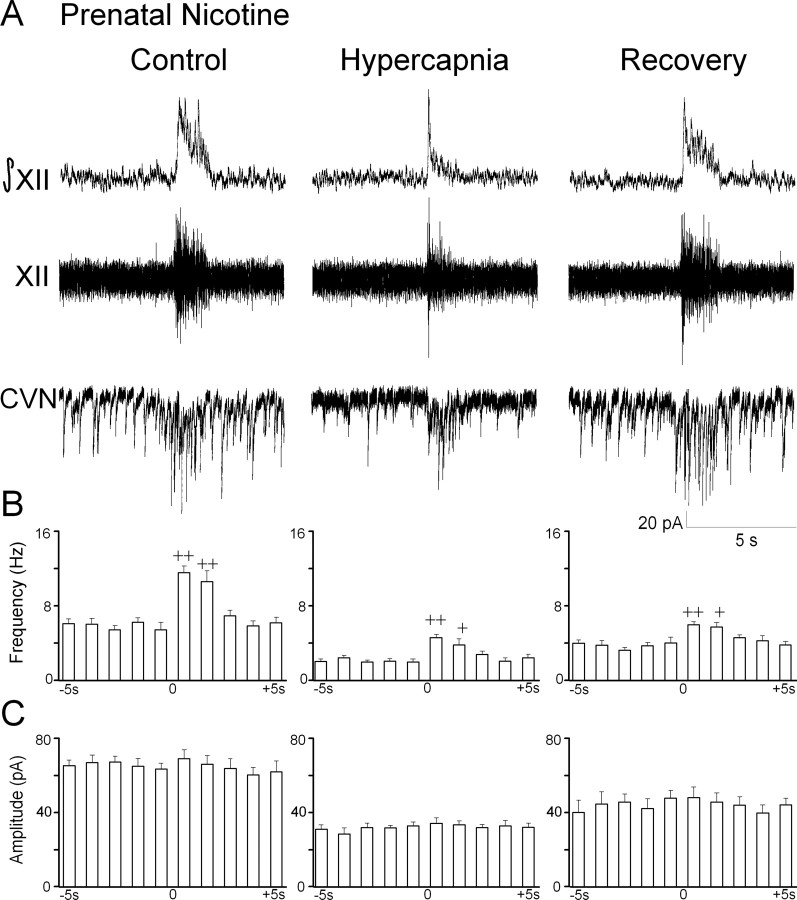
Figure 4.
Prenatal nicotine exposure exaggerates GABAergic IPSC frequency depression during hypercapnia. A, In animals exposed to nicotine prenatally, the inspiratory-evoked increase in GABAergic frequency was significantly increased compared with control animals, as shown in a typical experiment. B, Hypercapnia evoked a significant decrease in both spontaneous and inspiratory GABAergic IPSC amplitude. C, GABAergic IPSC amplitude was not modulated by respiratory bursts; however, hypercapnia diminished IPSC amplitude in animals exposed to nicotine prenatally. +p < 0.05; ++p < 0.01.