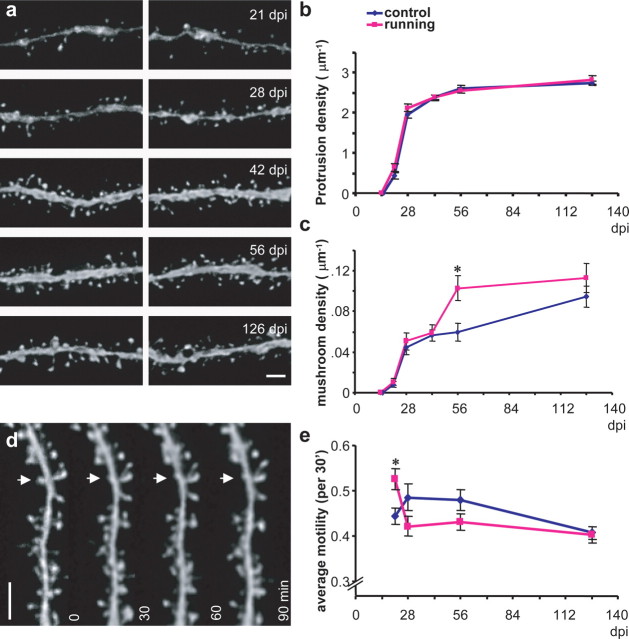
Figure 4.
The maturation of granule neurons born in the adult mouse brain: dendritic spine analyses. a, Representative images of dendritic segments from newborn neurons at 21, 28, 42, 56, and 126 d after viral infection. b, Quantification of total protrusion density. Blue indicates control; purple indicates running. The density of protrusions is expressed as the number of protrusions per micrometer of dendritic length. c, Quantification of mushroom spine density. Mushroom spines were identified if the estimated surface area (=π × Dmajor × Dminor/4) was ≥ 0.4μm2. The density of mushroom spines is expressed as the total number of mushroom spines per micrometer of dendritic length. d, An example of time-lapse series of a dendritic segment for spine motility analysis. The arrow indicates partial retractions of a spine over the time series. e, Quantification of spine motility. Data for b, c, and e are presented as mean ± SEM. The asterisks indicate where significant differences were seen between control and running mice (p < 0.01). Scale bars, 2μm.