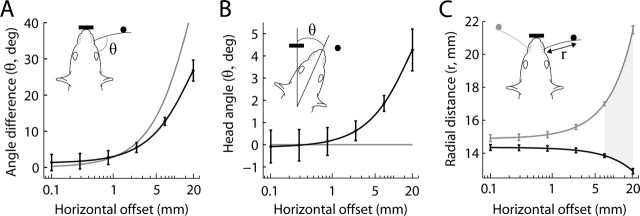
Figure 6.
Encoding of object location. A, Horizontal object offset versus the absolute difference in whisker angle, relative to head, during simultaneous contact of left and right whiskers with objects (black line). The gray line indicates the hypothetical relationship between horizontal and angular offset, assuming the head is at and perpendicular to the nose poke and that the whiskers have zero curvature. B, Head angle and horizontal offsets. Head angle was positive when oriented toward the pedestal (posterior pole). The black line shows best fit to head angle versus offsets, in which zero angle occurred when the rat was parallel to the axis of the nose poke. Positive values indicate movements toward the more posterior pole. The gray line indicates zero head angle. C, Relationship between horizontal offset and the radial point of contact. The radial location was computed as the distance of the pole from the whisker base (rather than the radial location along the shaft). The black line indicates radial point of contact with the posterior pole, and the gray line with the anterior pole. The gray filled region indicates horizontal offsets in which the difference in the radial point of contact along the whisker shaft was >3 mm. In A–C, all analyses include rats from all conditions (before and after trimming). Filled circles in the rat caricatures depict the vertical poles (black posterior and gray anterior), and the thick black bar indicate the nose poke. Black lines (plus gray in C) indicate the best quadratic fit to the data and the 95% confidence intervals.