Figure 3.
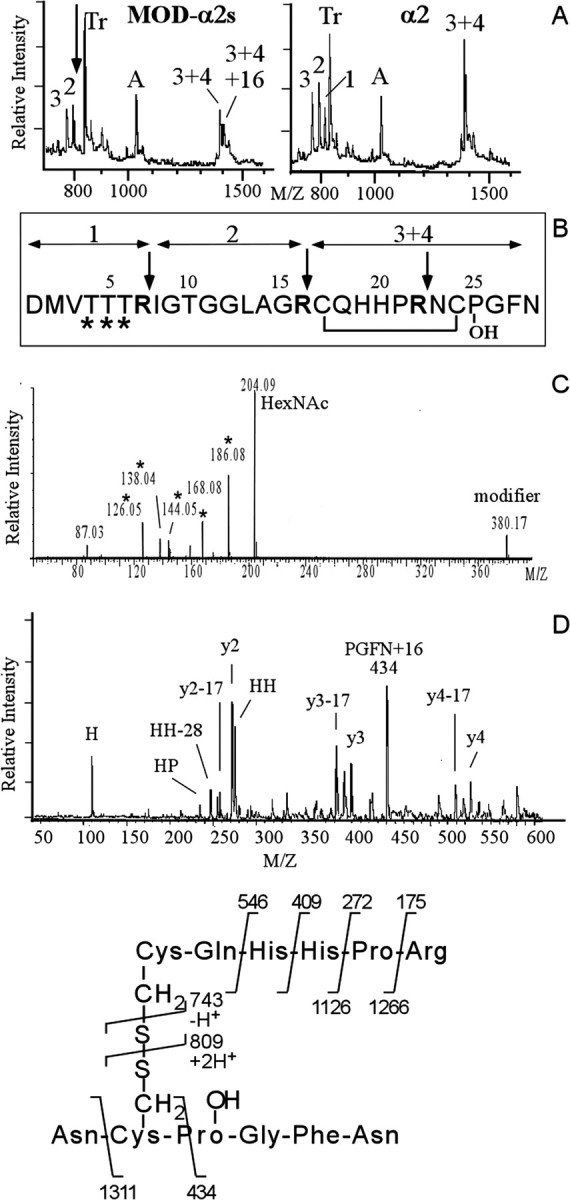
Structural characterization of the modifiedα2 peptides reveals multiple differentially glycosylated forms of the α2 peptide that in addition contains a HyP residue. A, MALDI mass spectra of a tryptic digest of the pooled modifiedα2 peptides F, F2, G, G2, H, and H2 (left) and synthetic α2 peptide (right). The arrow in A indicates the location of α2 tryptic peptide 1 that is expected to be modified (see B) and that has disappeared in the spectrum of the digested modified α2 peptides. Numbers indicate expected α2-specific tryptic peptides. Tr, Autoproteolytic fragments of trypsin. A, A-specific ion. B, Primary sequence of the α2 peptide. Trypsin cleaves after basic residues (indicated by the arrows), yielding four tryptic peptides. Fragments 3 and 4 are held together by a disulphide bridge. The sites predicted to be glycosylated are indicated by an asterisk. C, Electrospray MS/MS spectrum (the lower mass range) of purifiedα2 variant peptide F reveals glycosylation of F. Note the abundance of HexNac (at m/z of 204) and HexNac-related ions (m/z of 186, 168, 144, and 126). D, Identification of the 16 Da moiety on the modified α2 peptides as hydroxy-proline. Post-source decay spectrum (the lower mass range) of the trypsin digest fragment (3 + 4)+16 Da selected from the digest mixture of the pool of modifiedα2 peptides in A. The 16 Da mass addition is located to the four C-terminal residues PGFN, indicating a hydroxy-proline at position 25 instead of a proline residue. See E for the product assignments. Other fragment ions of the y- and a-series are indicated.
