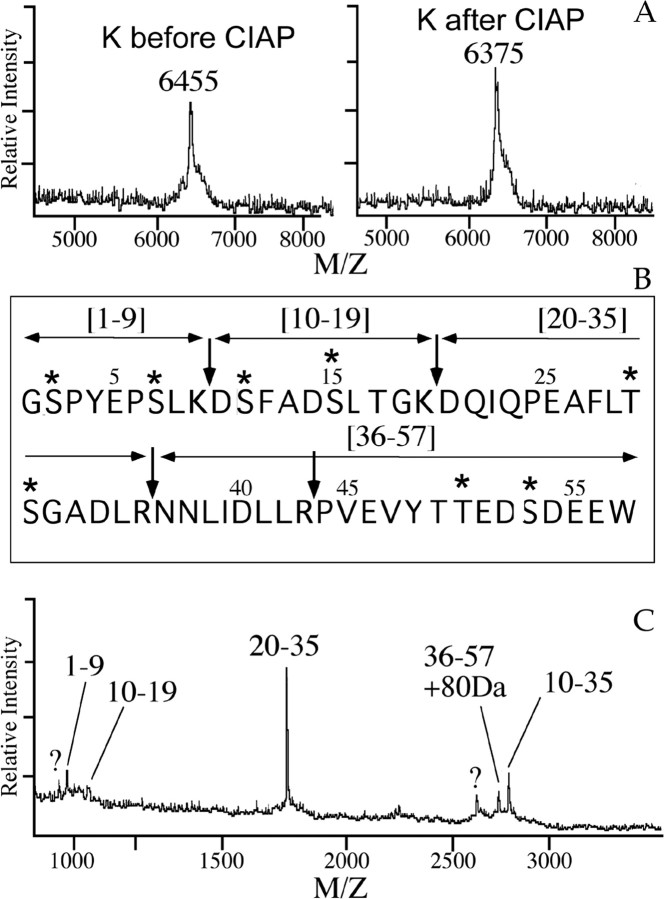
Figure 4.
Phosphatase treatment and tryptic peptide mapping of purified peptide K demonstrates phosphorylation of the C terminal of the β peptide. A, MALDI mass analysis of peptide K before (left) and after (right) dephosphorylation) using calf-intestine alkaline phosphatase (CIAP) shows removal of the 80 Da, phosphate moiety. B, Primary sequence of the β peptide. Trypsin cleaves after basic residues (indicated by the arrows), yielding five digest fragments, containing residues 1–9, 10–19, 20–35, 36–43, and 44–57, in case of a complete digestion. The putative phosphorylation sites are indicated with an asterisk. C, MALDI mass analysis of a tryptic digest of the phosphorylated β peptide (purified peptide K). Numbers indicate the residues of the trypsin fragments. Note the 80 Da mass addition to the partially cleaved C-terminal fragment 36–57. Unidentified molecular ions are labeled with a question mark.