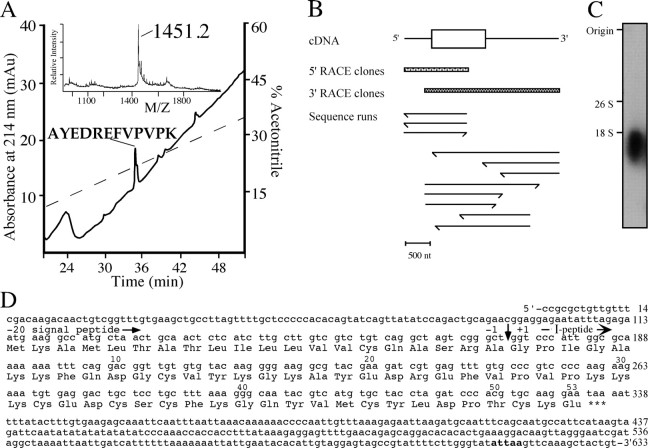
Figure 5.
Peptide mapping of purified molecule I, PCR strategy, and cDNA encoding peptide I. A, Purification of the endo-lys-c digested peptides of molecule I by reverse-phase HPLC. The main UV absorbing peak indicated contained the digest fragment of 1451.2 Da, which was subjected to amino acid sequence analysis. The dashed line indicates the gradient of acetonitrile. Inset in A, MALDI mass spectrum of the endo-lys-c digest of molecule I before purification. B, Schematic representation of the sequence strategy to obtain the cDNA of the peptide I. Both 5′ and 3′ RACE clones were sequenced in both orientations. Scale bar, 500 nt. C, Northern blot analysis of visceral and parietal ganglia shows a single band of 1.8 kb when hybridized to a peptide I-specific random labeled [γ-32P]dATP probe. The transcript size markers (yeast ribosomal RNAs) 26S (3400 bases) and 18S (1800 bases) are indicated. D, Nucleotide sequence and deduced amino acid sequence of peptide I cDNA. The number of nucleotides is indicated at the end of each line. Amino acid sequence number of peptide I starts at the predicted N-terminal residue (vertical arrow) and is indicated above the sequence. The consensus for polyadenylation is shown in bold.