Figure 2.
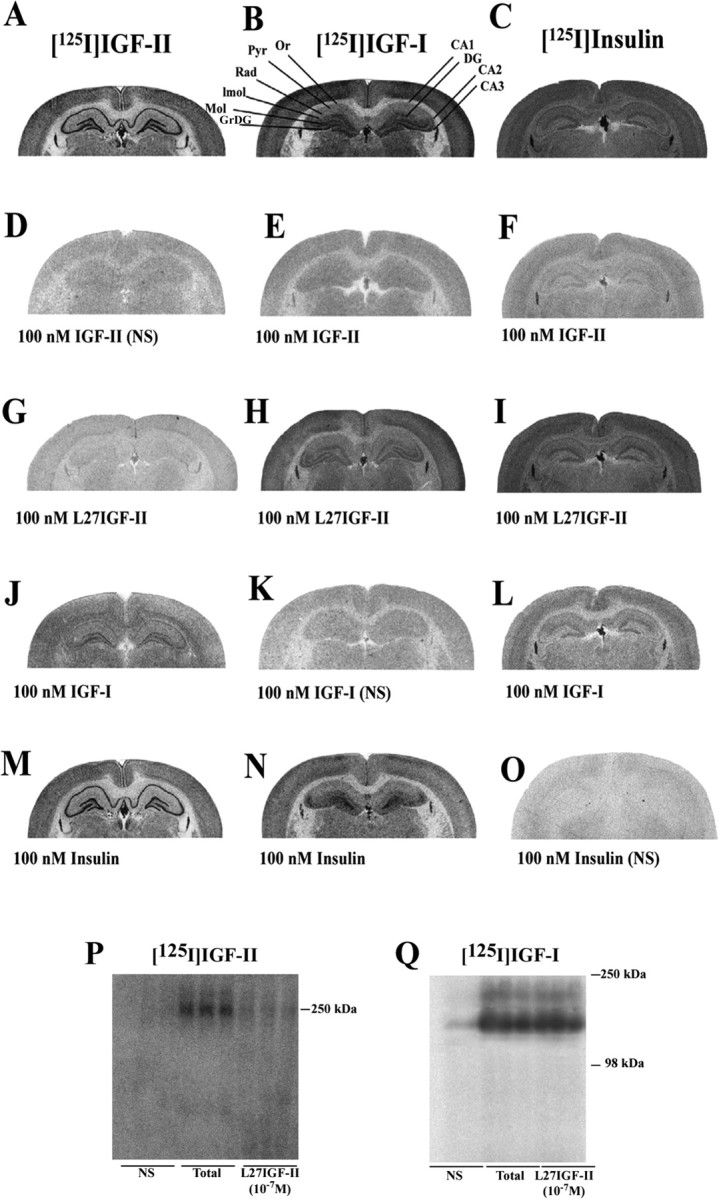
A-Q, Photomicrographs showing the autoradiographic distribution of [125I]IGF-II (A, D, G, J, M), [125I]IGF-I (B, E, H, K, N), and [125I]insulin (C, F, I, L, O) binding sites in the absence or presence of 100 nm IGF-II, Leu27IGF-II (L27IGF-II), IGF-I, and insulin in the adult rat hippocampus. [125I]IGF-II binding in the hippocampus was competed potently by IGF-II > Leu27IGF-II > IGF-I (D, G, J) but not much by insulin (M). [125I]IGF-I binding was competed potently by IGF-I > IGF-II > insulin > Leu27IGF-II (K, E, N, H). [125I] Insulin binding was competed by insulin > IGF-II > IGF-I ≫ Leu27IGF-II (O, F, L, I). P, Q, Affinity cross-linking of [125I]IGF-II (P) and [125I]IGF-I (Q) to rat hippocampal membranes showing that Leu27IGF-II displaces radiolabel from the 250 kDa band corresponding to the IGF-II/M6P receptor but not from the 240 or 135 kDa bands bound by [125I]IGF-I. NS, Nonspecific binding; Or, stratum oriens; Pyr, pyramidal cell layer; Rad, stratum radiatum; lmol, stratum lacunosum moleculare; Mol, molecular layer of the DG; GrDG, granular cell layer of the DG.
