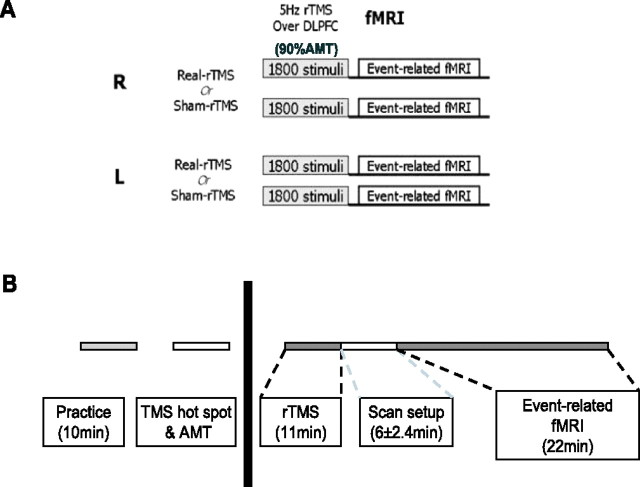
Figure 1.
Experimental design for the fMRI study. A, Subjects attended on four separate sessions in which they received real and sham 5 Hz rTMS conditioning to their right and left DLPFC, followed by a 20 min fMRI scanning session. Subjects were allocated to each session in a counterbalanced order. B, Description of each individual session. Subjects had a 10 min practice session to ensure familiarity with the task, followed by all of the procedures before rTMS conditioning (left): motor hot spot identification, marking of the DLPFC site to be stimulated, and measurement of the AMT. These were all performed in a separate testing room outside of the scanner. After rTMS, subjects were wheeled into the scanner room with an MRI-compatible wheelchair and set up to begin fMRI scanning. This took on average 6 ± 2.4 min, accounting for the time to scout and allow the scanner to perform shimming before fMRI data acquisition.