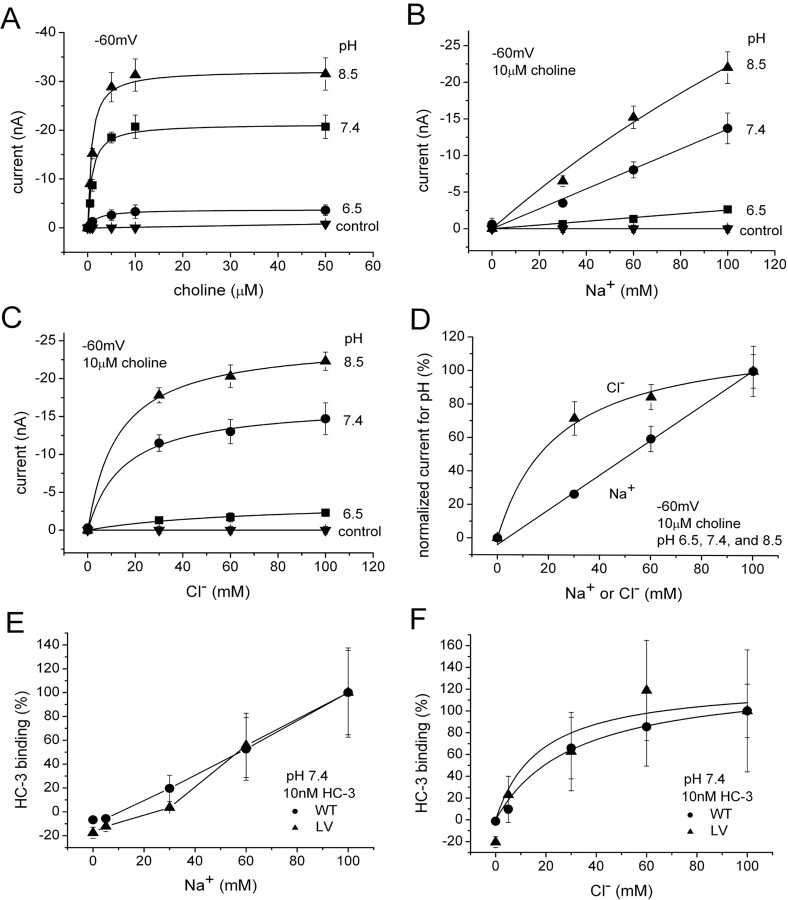
Figure 8.
Effect of pH on K m and I max. A, K m and I max for choline-induced currents measured at different pH and held at −60 mV (n = 3). At pH 6.5, K m of 1.9 ± 0.3 μm and I max of −3.8 ± 0.1 nA. At pH 7.4, K m of 0.9 ± 0.3 μm and I max of −21.3 ± 0.4 nA. At pH 8.5, K m of 0.8 ± 0.2 μm and I max of −32.3 ± 0.5 nA. LV-expressing oocytes were used. As a control, three water-injected oocytes were measured at each pH 6.5, 7.4, and 8.5. B, Na+ dependence of choline-induced current at various pH. In 10 μm choline, the induced current was measured at −60 mV, because LiCl replaced NaCl at different pH (n = 3). The Na dependence is linear at all pH. LV-expressing oocytes were used. C, Cl− dependence of choline-induced current at various pH (n = 3). In 10 μm choline, the induced current at −60 mV is measured at different pH (Na gluconate replacing NaCl). Results at 6.5 were insufficiently precise, although saturation clearly occurs. K m of 67.2 ± 22.5 mm and I max of −3.8 ± 0.6 nA for pH 6.5. K m of 14.9 ± 3.4 mm and I max of −16.7 ± 0.7 nA for pH 7.4. K m of 12.8 ± 1.7 mm and I max of −25.0 ± 0.5 nA for pH 8.5. LV-expressing oocytes were used. D, Na+ and Cl− dependence of the choline-induced current do not depend on pH. Data from B and C are normalized for all pH and averaged. For Cl−, K m of 23.6 ± 5.8 mm and I max of 122.2 ± 7.6%. E, Na+ dependence of HC-3 binding (n = 6–8). Na+ dependence of HC-3 binding is similar to that of choline-induced current (D). F, Cl− dependence of HC-3 binding (n = 6–8). Cl− dependence of HC-3 binding is similar to that of choline-induced current (D). Cl− dependence is fitted to a single-binding-site model. K m of 31.2 ± 3.8 mm and B max of 131.0 ± 4.8% for WT. K m of 17.5 ± 20.4 mm and B max of 126.4 ± 30.7% for LV.