Figure 3.
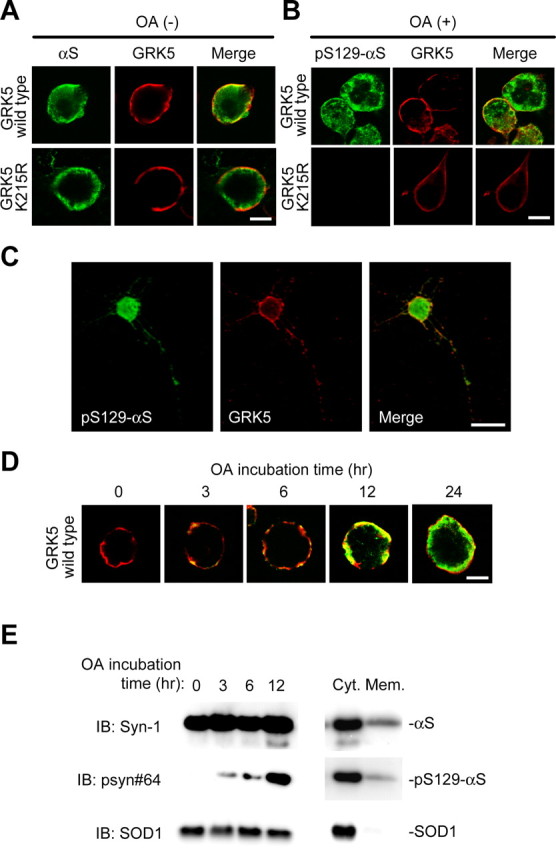
αS colocalizes with GRK5 at the plasma membrane of HEK293 cells. A, B, HEK293–αS cells were transiently transfected with either wild-type GRK5–FLAG (top) or GRK5–K215R-FLAG (bottom) and incubated in the presence (B) or absence (A) of OA. Fixed cells were processed for direct immunofluorescence with polyclonal anti-GRK5 antibody (H-64) (A and B, red channel) and either monoclonal anti-αS antibody (LB509; A, green channel) or monoclonal anti-pS129–αS antibody (psyn#64; B, green channel). In HEK293–αS cells expressing GRK5, αS and GRK5 colocalized in the area of the plasma membrane (A, top), and pS129–αS was distributed in the areas of the perikarya and plasma membrane (B, top). In the cells expressing mutant GRK5–K215R, there was no fluorescence of pS129-αS, although the distribution of GRK5–K215R was similar to that of wild-type GRK5 (B, bottom). Scale bars, 10 μm. C, Phosphorylation of αS by GRK5 in primary neurons from the cerebral cortex of fetal mice. The primary cortical neurons were cotransfected with wild-type αS and GRK5 cDNAs, treated with 10 nm OA for 12 h, and immunostained with anti-pS129–αS (psyn#64; left) and anti-GRK5 (H-64; middle) antibodies. A merged image is shown at right. Scale bar, 20 μm. D, Translocation of pS129–αS catalyzed by GRK5. HEK293–αS cells were transiently transfected with wild-type GRK5–FLAG cDNA, and the cells were incubated with 20 nm OA for various time periods. Fixed cells were immunostained with anti-GRK5 (H-64; red) and anti-pS129–αS (psyn#64; green) antibodies. After 3 h of incubation, pS129–αS was detected in the area of the plasma membrane. With time, pS129–αS was gradually translocated from the plasma membrane to the perikaryal area. Scale bar, 10 μm. E, Immunoblotting (IB) of the cytosol and membrane fractions of HEK293–αS cells transiently transfected with wild-type GRK5 cDNA. After incubation of the cells with 20 nm OA for various time periods, the cells were disrupted, and the homogenate was sequentially centrifuged at 800 × g for 10 min and at 100,000 × g for 30 min. The fractions were tested for the presence of pS129–αS by immunoblotting. In the presence of OA, the amount of pS129–αS in the cytosol fraction gradually increased with time, although the expression levels of the total αS and SOD1 were constant (left). In the same preparation of cell homogenate at 12 h of OA incubation, the amount of pS129–αS in the cytosol fraction (Cyt.) was much larger than that in the membrane fraction (Mem.; right). Abundant SOD1 was detectable in the cytosol fraction.
