Figure 9.
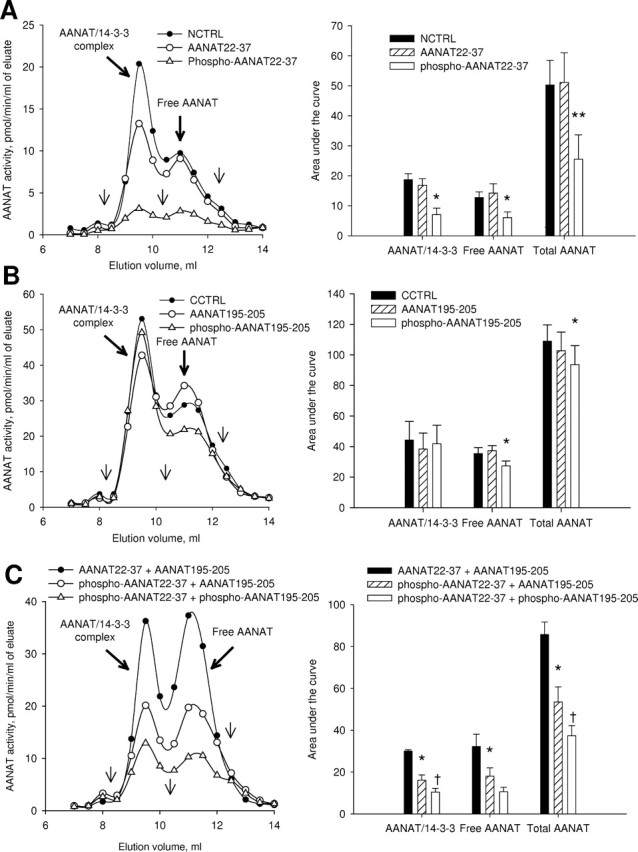
The role of Thr-29 and Ser-203 phosphorylation in the formation of AANAT/14-3-3 complex. After homogenization in ammonium acetate buffer and centrifugation at 15,000 × g for 10 min supernatant fractions from dark-adapted nighttime retinas were incubated in the presence of 100 μm phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated AANAT-specific peptides (Table 1) for 16 h at +4°C and separated by FPLC on a Superdex 75 10/300 GL column. Scrambled peptides were used as a control. Representative FPLC profiles, peak square data, and statistical evaluation are shown for each treatment. The thin arrows on FPLC profiles indicate the location of molecular weight standards; from left to right: 128 kDa, 44 kDa, and 17 kDa. A, N-terminal AANAT-specific and control (NCTRL) peptides. B, C-terminal AANAT-specific and control (CCTRL) peptides. C, Combination of N-terminal and C-terminal AANAT-specific peptides. *p < 0.05 when compared with scrambled peptide control group; †p < 0.05 when compared with phospho-AANAT22–37 + AANAT195–205 group; Student–Newman–Keuls method following one-way RM-ANOVA, p < 0.01. Values are means ± SEM (n = 3).
