Figure 3.
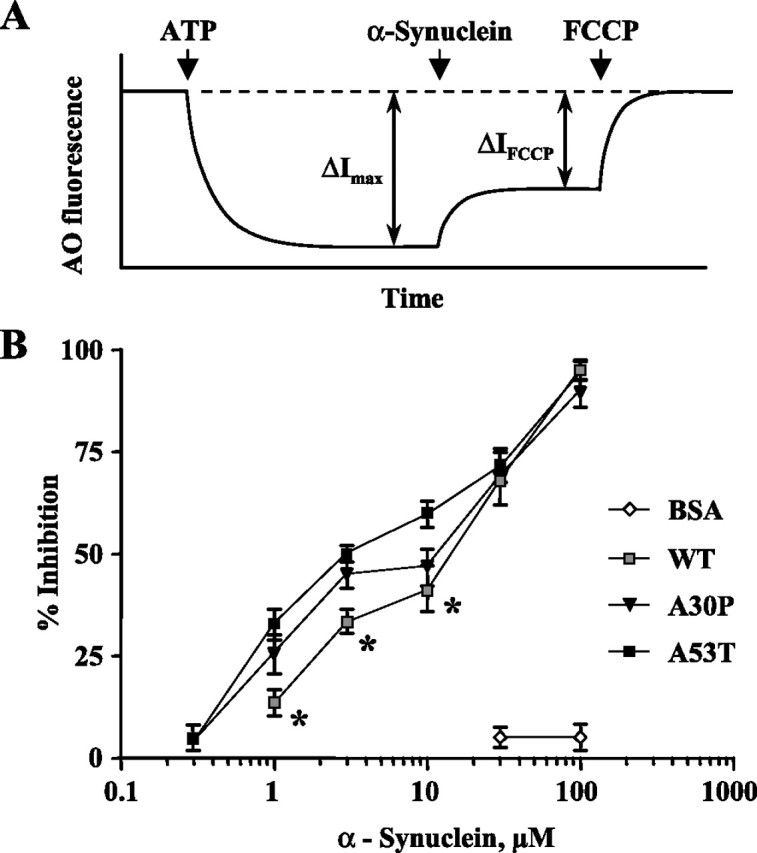
α-Synuclein induces a leakage of protons from isolated bovine chromaffin granules. A, Protocol used to measure the degree of proton leakage from chromaffin vesicles. H+-ATPase inhibitor bafilomycin (10 nm; dashed line) and the protonophore FCCP (1 μm) were used to completely collapse vesicular pH. Addition of ATP in the presence of AO resulted in fluorescence quenching caused by the dye uptake into the vesicles. ΔI max, maximal ATP-dependent vesicle acidification; ΔI FCCP, the change in fluorescence intensity as a result of FCCP. B, Concentration dependence of α-synuclein-induced proton leakage from the vesicles, which was calculated as (ΔI max − ΔI FCCP) × 100/ΔI max for each protein concentration. The curve for A53T α-synuclein is significantly different from WT (p < 0.0001), and the curve for A30P is significantly different from WT α-synuclein in the 0.3–10 μm range (*p < 0.05) by two-way ANOVA test.
