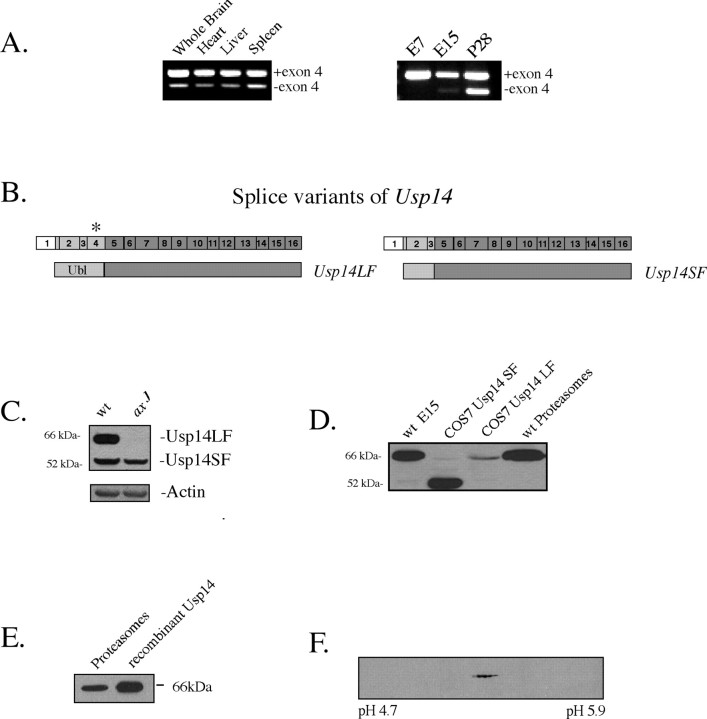
Figure 1.
Usp14 is alternatively spliced. A, The left panel depicts Usp14 RT-PCR products from tissues of adult (P64) mice, and the right panel shows the Usp14 RT-PCR products from E7 and E15 embryos and whole brain from P28 wild-type mice demonstrating the two forms of Usp14 produced from the alternative splicing of exon 4. Primers flanking exon 4 were used for amplification of reverse-transcribed cDNAs. B, Schematic diagram of the cDNAs isolated from brain. The full-length cDNA is referred to as Usp14LF, and the splice variant lacking exon 4 (asterisk) is referred to as Usp14SF. C, Immunoblot analysis of 6-week-old wild-type (wt) and axJ brains demonstrating the two forms of Usp14. Blots were probed with polyclonal antisera to Usp14 and reprobed for β-actin as a loading control. D, Immunoblot analysis demonstrating the different migration patterns of Usp14LF and Usp14SF expressed from wild-type E15 embryos, COS-7 cells transfected with expression vectors for Usp14LF or Usp14SF, and neuronal proteasome fractions from wild-type (P28) mice. Blots were probed with polyclonal antisera to Usp14. E, Immunoblot of Usp14 showing the similar migration pattern between recombinant Usp14 and Usp14 found in neuronal proteasomes from wild-type mice. Blots were probed with polyclonal antisera to Usp14. F, Two-dimensional electrophoresis gel of proteasome fractions from wild-type mice immunoblotted with polyclonal antisera to Usp14.