Figure 1.
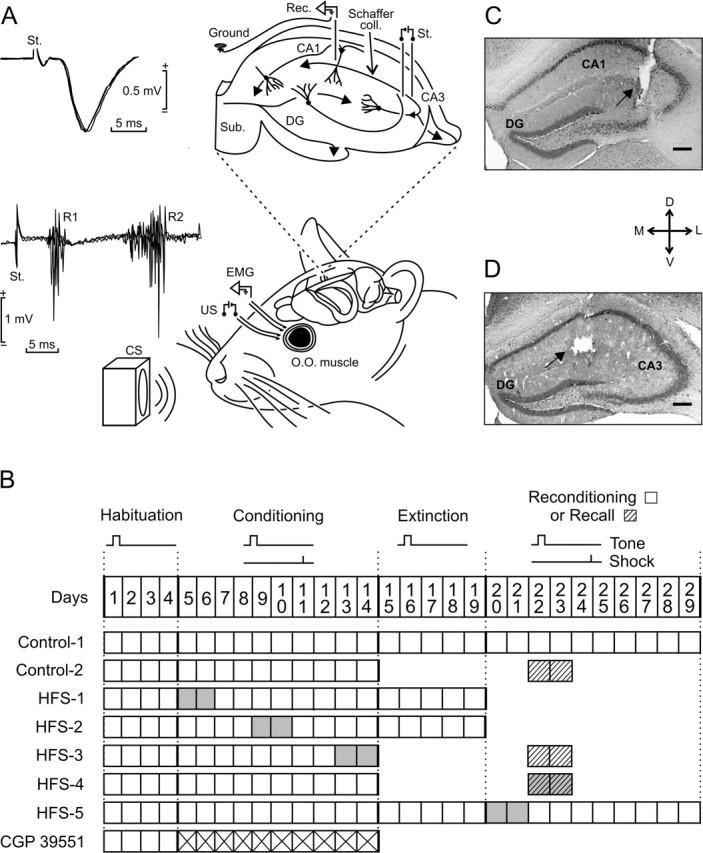
Experimental design. A, EMG recording electrodes were implanted in the orbicularis oculi (O.O.) muscle of the upper left eyelid. Bipolar stimulating electrodes were implanted on the ipsilateral supraorbitary branch of the trigeminal nerve for presentation of US. For classical conditioning of eyelid responses, we used a tone (20 ms; 2.4 kHz; 85 dB) as a CS. The loudspeaker was located 30 cm from the animal’s head. As shown at the top right diagram, animals were also implanted with stimulating and recording electrodes aimed to activate CA3–CA1 synapses of the right (contralateral) hippocampus. The two superimposed recordings at the top left illustrate the extracellular synaptic field potential recorded (Rec.) at the stratum radiatum of the CA1 area after electrical stimulation (St.) of the Schaffer collaterals. Superimposed recordings at the bottom left correspond to the blink reflex evoked at the O.O. muscle by the electrical stimulation of the trigeminal nerve. Note the two short (R1) and long (R2) latency components characterizing the blink reflex in mammals. B, Main experimental groups. All animals received four habituation and 10 conditioning sessions. In addition, some groups received five extinction or two recall (dashed boxes) sessions. Two groups (Control-1 and HFS-5) were reconditioned for 10 d. The CGP 39551 group received this drug daily during the 10 conditioning sessions (crossed boxes). Gray boxes indicate when the HFS sessions were applied. C, D, Photomicrographs illustrating the location of stimulating (C) and recording (D) sites (arrows). Scale bars: C, D, 200 μm. D, Dorsal; L, lateral; M, medial; V, ventral; DG, dentate gyrus; Sub, subiculum.
