Figure 6.
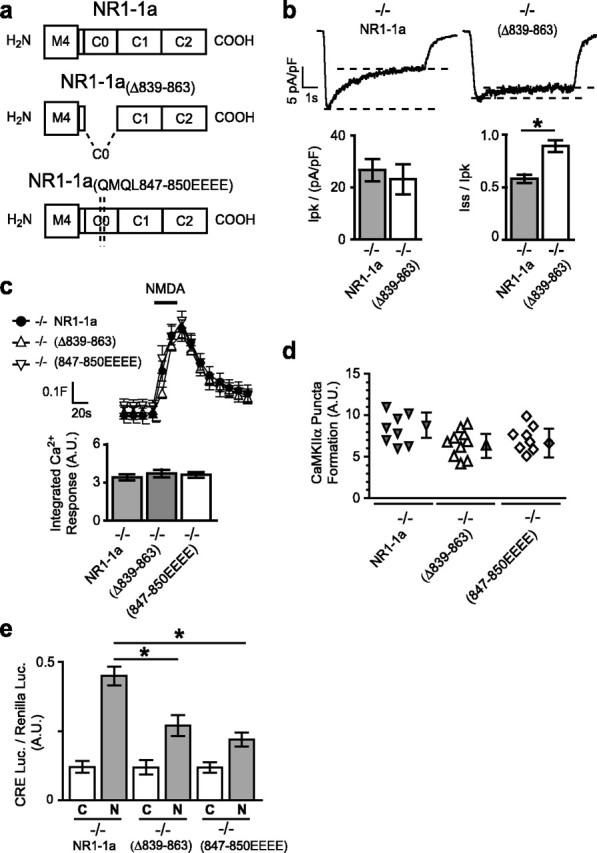
Deletion of the C0 domain or mutation of a single CaM-binding site significantly reduces gene expression. a, C-terminal domains of NR1–1a, NR1–1aΔ839–863, and NR1–1a(QMQL847–850EEEE). b, Sample traces of whole-cell currents induced by NMDA (100 μm for 5 s) for neurons transfected with NR1–1a or NR1–1aΔ839–863. Quantification of the normalized peak current revealed no significant difference between NR1−/− neurons transfected with NR1–1a or NR1–1aΔ839–863; steady-state currents were higher for NR1–1aΔ839–863 than for NR1–1a because of reduced inactivation. c, Reconstituted [Ca2+]i responses to NMDA have similar profiles in NR1−/− neurons transfected with NR1–1aΔ839–863, NR1–1a(QMQL847–850EEEE), or NR1–1a (mean ± SEM fura-2 ratio for 12 neurons). The column graphs show the quantification of integrated area of [Ca2+]i responses; each condition represents the mean ± SEM for at least 12 neurons from at least four embryos. d, No significant difference was observed in NMDA-induced puncta formation by GFP-CaMKIIα in neurons transfected with NR1–1a, NR1–1aΔ839–863, or NR1–1a(QMQL847–850EEEE). e, NMDA-induced CRE-dependent luciferase gene expression is significantly reduced in NR1−/− neurons transfected with NR1–1aΔ839–863 or NR1–1a(QMQL847–850EEEE). Mean ± SEM for at least four independent experiments. *p < 0.01, unpaired t test. A.U., Arbitrary units; C, control; N, NMDA.
