Figure 3.
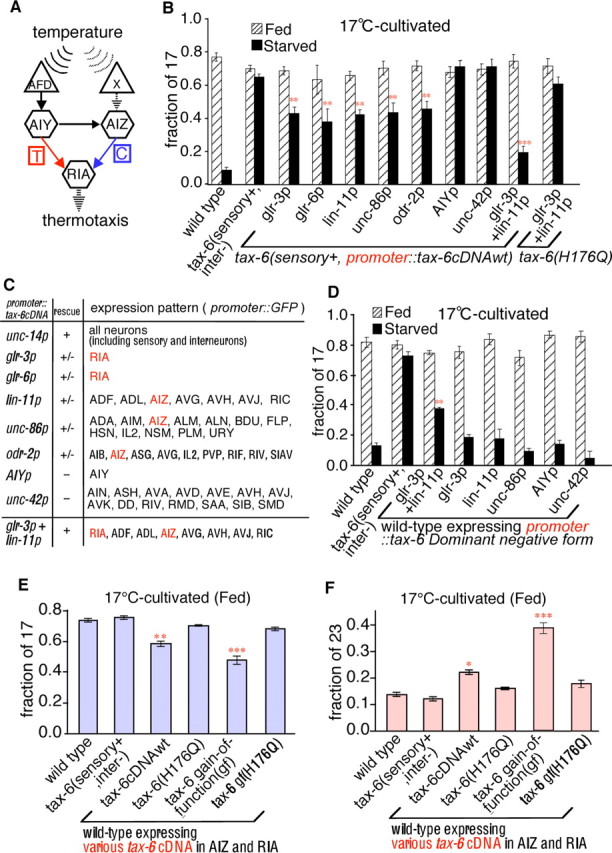
Essential interneurons for TAX-6/calcineurin-mediated thermotactic associative learning. A, Schematic diagram of the neural circuit underlying thermotaxis (Mori and Ohshima, 1995). A temperature signal is sensed by the AFD and unidentified X thermosensory neurons; it is then transmitted to AIY and AIZ interneurons, and then finally integrated in the RIA interneuron. The AIY thermophilic (T) and AIZ cryophilic (C) arms of the circuit mediate movement to higher (red) and lower (blue) temperatures, respectively. B, Rescue experiments of defective temperature-feeding state associative learning in the tax-6 mutant. Each bar represents the average of at least three independent thermotaxis assays using 20 animals per assay. Two or three independent transgenic lines were tested for tax-6(sensory+) animals expressing tax-6cDNAwt driven by various promoters. For wild-type and tax-6(sensory+, inter−), n = 120. For each tax-6(sensory+, promoter::tax-6cDNAwt) transgenic line, n ≥ 100. C, Summary for rescue experiments of defective associative learning between temperature and feeding state of tax-6 mutant. D, The effect of the TAX-6 dominant-negative form on thermotaxis. Each bar represents the average of at least three independent thermotaxis assays using 20 animals per assay. Three independent transgenic lines were tested for tax-6(sensory+) animals expressing the tax-6 dominant-negative form driven by various promoters. n ≥ 120 animals for each genotype. E, F, Results of the thermotaxis assay conducted at 17 (E) or 23°C (F) on 17°C-cultivated fed wild-type animals carrying various types of tax-6 cDNA in AIZ and RIA interneurons. H176Q indicates the TAX-6 phosphatase negative form. Each bar represents the average of at least three independent thermotaxis assays using 20 animals per assay. Three independent transgenic lines were tested wild-type animals expressing various tax-6 cDNAs. n ≥ 80 animals for each genotype.
