Figure 4.
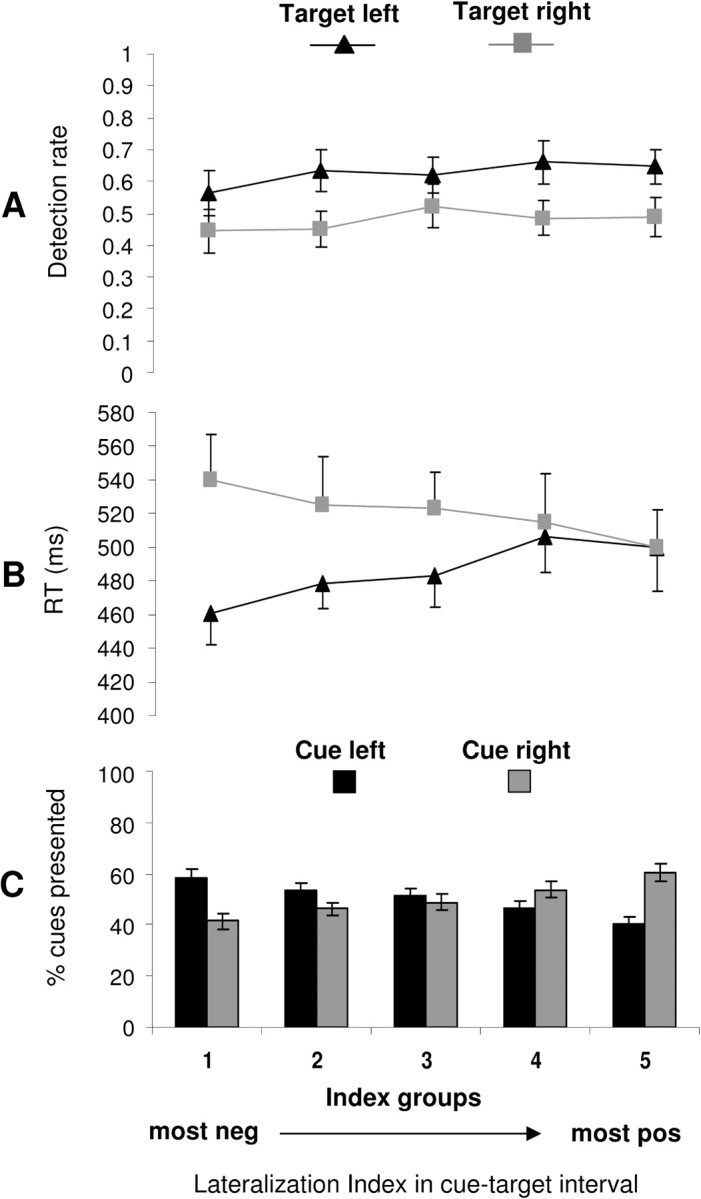
Trial-by-trial variability in pretarget α index versus behavior. A, Average detection rates of left and right targets (±SE). B, Average reaction times to left and right targets (±SE). C, Distribution of left and right cue trials (mean ± SE) are displayed as a function of α-lateralization index before target onset (collapsed over second half of the cue–target interval), subdivided in five index groups. Each index group comprises data of at least 30 trials from each of the 10 subjects. The α-lateralization index is related to reaction time (B) but not detection rate (A) of forthcoming targets. Note the overall advantage for detection of left compared with right targets, both in terms of detection rates and reaction times, which might be attributable to “pseudoneglect,” the natural tendency of neurologically normal subjects to attend more easily to the left than to the right visual hemifield (see Results, Behavior: overall asymmetry in left versus right visual field processing). neg, Negative; pos, positive.
