Figure 1.
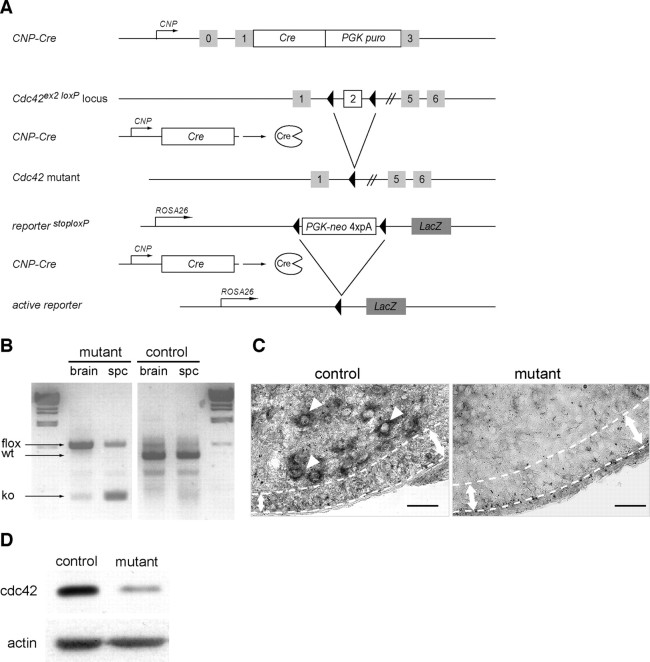
Recombination of the conditional Cdc42 allele in the CNS of mutant mice. A, Schematic representation of the Cnp-Cre knock-in allele, the conditional Cdc42 allele, and the reporter LacZ allele. After Cnp-Cre-mediated recombination, the genomic region between the two LoxP sites is excised, inactivating the Cdc42 gene and triggering the expression of the enzyme β-galactosidase in recombined oligodendrocyte cells. B, PCR shows the recombination of the conditional Cdc42 allele on genomic DNA isolated from 1-d-old control (Cnp-Cre− Cdc42lox/wt) and mutant (Cnp-Cre+ Cdc42lox/lox) brain and spinal cord. The fragment sizes for wild-type (wt), Cdc42 floxed (flox), and Cdc42 mutant (KO) alleles are indicated. C, In situ hybridization with a riboprobe complementary to the full-length Cdc42 cDNA failed to detect a Cdc42 signal in spinal motoneurons (arrowheads) or in the ventral developing white matter of P2 mutant mice (area between dotted lines). Scale bar, 50 μm. D, Western blot analysis shows a marked decrease of cdc42 protein expression in mutant OPC cultures. The remaining cdc42 signal detected is likely caused by some contaminating astrocytes and nonrecombined OPCs in these cultures. PGK puro, Phosphoglycerate kinase puromycin; PGK-neo, phosphoglycerate kinase neomycin.