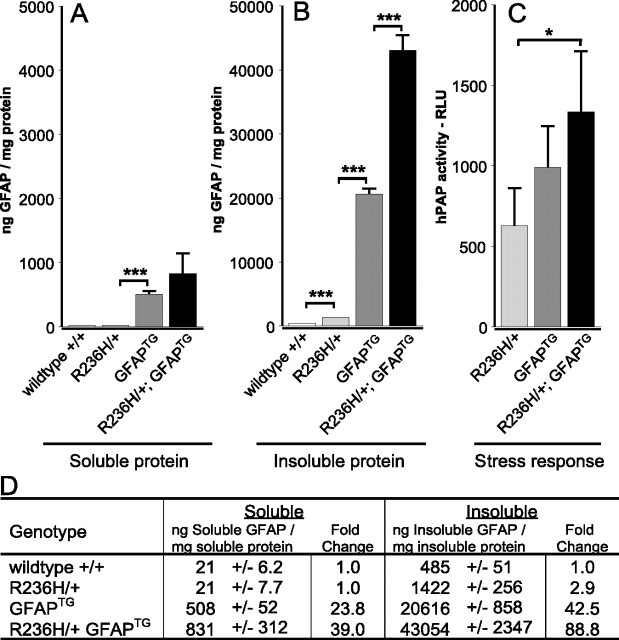
Figure 9.
Elevated levels of insoluble GFAP and an increased stress response in R236H/+;GFAPTG mice. A, B, Brains from wild-type, R236H/+,GFAPTG, and R236H/+;GFAPTG animals were analyzed at P24 by ELISA to quantitate GFAP protein levels in the soluble (A) and insoluble (B) pools. D, GFAPTG mice show an increase in both soluble and insoluble GFAP compared with mutant mice, and R236H/+;GFAPTG show an additional increase of insoluble GFAP compared with GFAPTG animals. C, R236H/+;GFAPTG mice have an increased CNS stress response. Brain homogenates were taken from the progeny of R236H/+ mice crossed with GFAPTG mice with the ARE-hPAP reporter transgene to quantify the stress response at P25. Reporter activity in R236H/+;GFAPTG mice was increased over the response observed in the R236H/+ mice (*p = 0.02). Differences in reporter activity between R236H/+ and GFAPTG mice, and GFAPTG mice and R236H/+; GFAPTG mice were not significant. n = 4 for each group; *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001. Error bars indicate SD.