Figure 4.
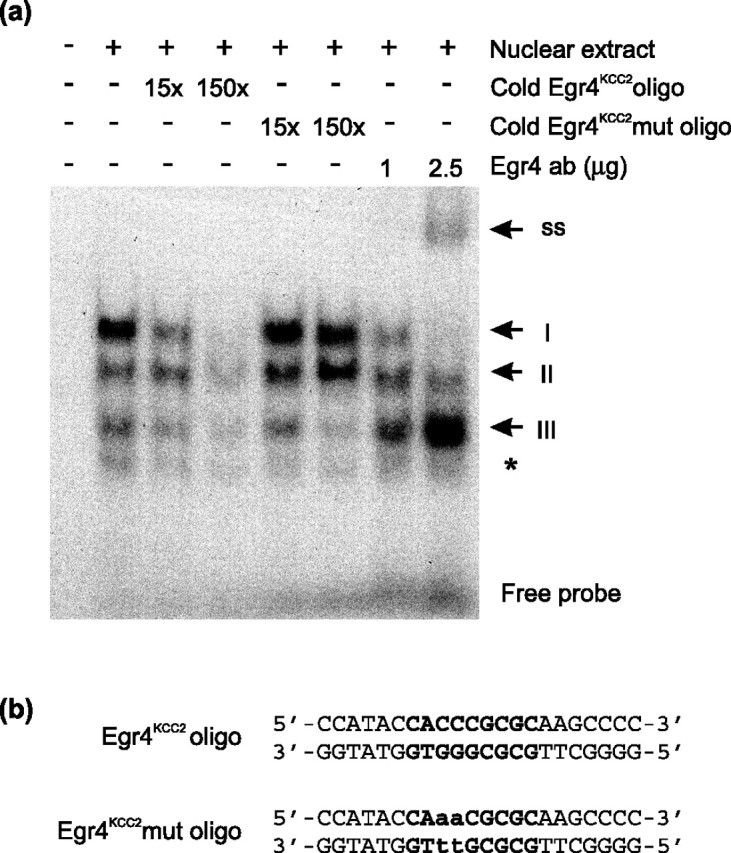
Egr4 binds the Egr4KCC2 element in vitro. a, Three specific complexes (I–III) are detected in EMSA, using labeled oligonucleotides bearing a single copy of the Egr4KCC2 element and nuclear extracts of N2a cells transfected with Egr4 expression plasmid. Complex I is competed effectively by cold Egr4KCC2 oligonucleotides. In contrast, unlabeled Egr4KCC2mut oligonucleotides do not influence the formation of complex I. The addition of Egr4 antibody prevents complex I formation in a dose-dependent manner and results in the formation of a new supershifted complex (indicated by ss). Complex II is affected less by Egr4KCC2 oligonucleotides and not at all by Egr4KCC2mut oligonucleotides. Complex III is competed by both wild-type and mutant Egr4KCC2 oligonucleotides. Note the significant increase in complex III intensity after the addition of the Egr4 antibody. Nonspecific binding is indicated by an asterisk. b, Sequences of Egr4KCC2 and Egr4KCC2mut oligonucleotides used in EMSA. The Egr4KCC2 sequence is highlighted in bold. Mutated nucleotides are shown in small case letters.
