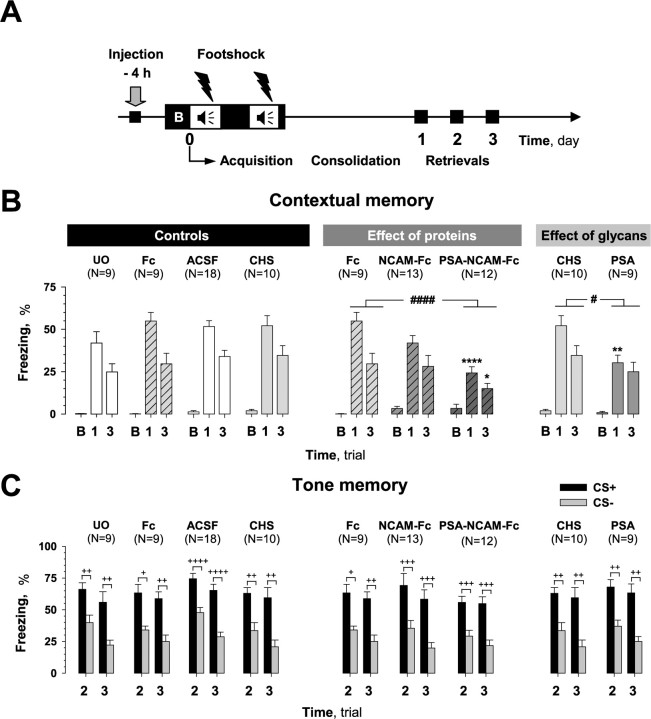
Figure 2.
Effects of pretraining injection of compounds on fear conditioning. A, Scheme showing manipulations performed in this series of experiments. Compounds were injected 4 h before training. A 100 s trial (B) was used to evaluate the baseline response to the conditioned context (CC+) before training. B, Pretraining injection of PSA-NCAM-Fc or PSA, but not NCAM-Fc, impaired contextual memory when tested on the first (both compounds) and third (PSA-NCAM-Fc only) days after training (trials 1 and 3, respectively). Mice injected with the Fc-fragment (Fc) and chondroitin sulfate (CHS) served as controls. Fc- and chondroitin sulfate-injected mice did not differ in contextual memory from unoperated (UO) and ACSF-injected mice, respectively. Fear memory was measured as the percentage of time that mice spent in the freezing state. Analysis of freezing during baseline trial B showed no difference between injected groups. C, Pretraining injection of tested compounds did not affect freezing time in response to paired (CS+) and unpaired (CS−) tones during trials 2 and 3. Discrimination between CS+ and CS− tones was also not different between injected groups. #p ≤ 0.05, ####p ≤ 0.001 (the effect of treatment by two-way ANOVA); *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ****p ≤ 0.001 (post hoc FLSD test, as compared with corresponding controls, Fc or chondroitin sulfate, for corresponding days); +p < 0.05, ++p < 0.01, +++p < 0.005, ++++p < 0.001 (Wilcoxon test).