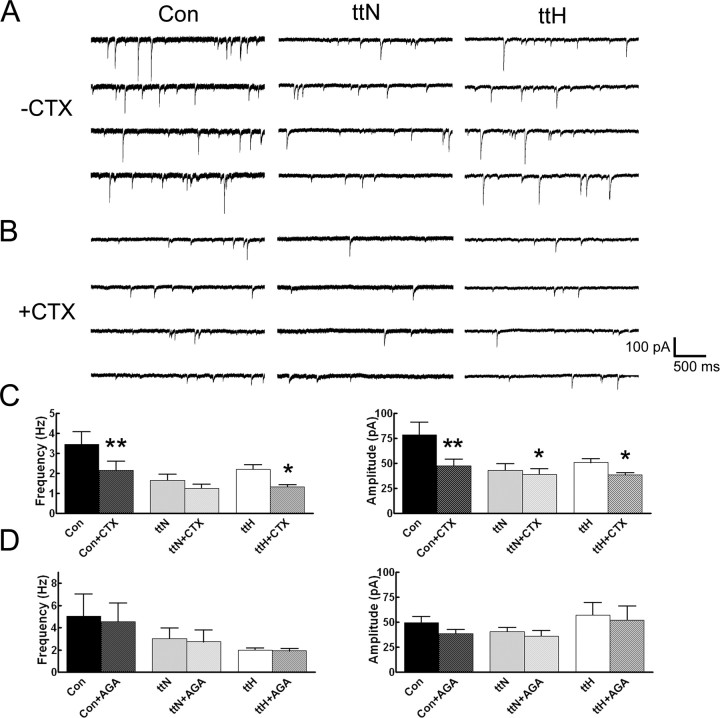
Figure 4.
N-type calcium channels are functional in inhibitory presynaptic terminals in both control and tish cortices. A, B, Representative recordings from control, tish normotopic, and tish heterotopic neurons demonstrate reduced sIPSC properties in response to incubation with the N-type calcium channel-specific blocker ω-conotoxin-GVIa. C, Group data analyses reveal a significant reduction in sIPSC frequency in control and tish heterotopic neurons in response to ω-conotoxin-GVIa. The amplitude of sIPSCs was significantly reduced in all groups. D, Group data analyses demonstrate that sIPSCs are unchanged in all three groups in response to incubation in the P/Q-type calcium channel-specific blocker ω-agatoxin-IVa. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (Student's t test). Con, Control; ttN, tish normotopic; ttH, tish heterotopic; CTX, ω-conotoxin-GVIa; AGA, ω-agatoxin-IVa.