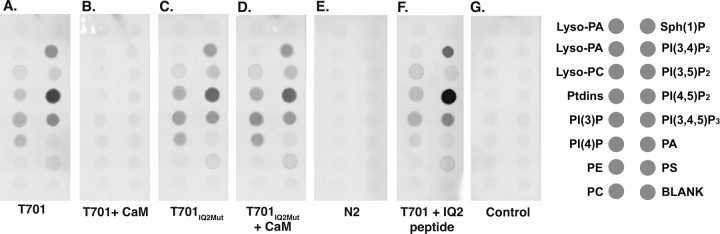
Figure 3.
Binding of Myo1c fragments to anionic phospholipids. A–F, Each panel shows one PIP-strip, a nitrocellulose membrane, which has been spotted with anionic lipids, that has been incubated with the indicated Myo1c fragment. Bound Myo1c fragments were detected by virtue of the N-terminal Xpress epitope tag. The diagram to the right indicates the location and identity of the anionic lipids. A, T701-Myo1c binds weakly to several of the anionic lipids and strongly to PI(4,5)P2 (PIP2). B, The addition of excess CaM abolishes Myo1c-T701 interactions with anionic lipids. C, Myo1c-T701IQ2Mut binds to the same subset of anionic lipids as Myo1c-T701. D, Excess CaM does not block the interactions of Myo1c-T701IQ2Mut with anionic lipids. E, Myo1c-N2 does not bind anionic lipids. F, Excess IQ2 peptide, when incubated with Myo1c-T701, does not block the binding of Myo1c-T701. G, Antibody only control.