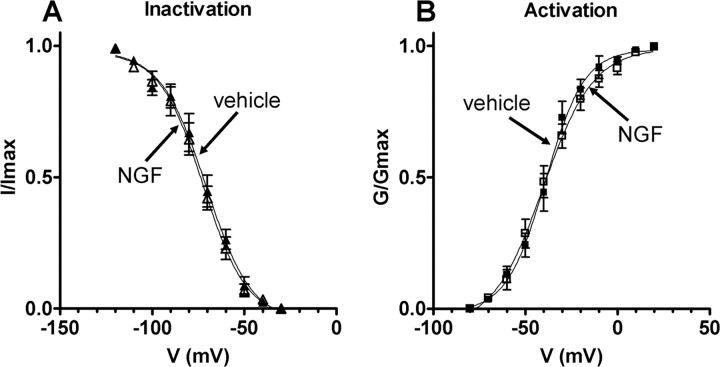
Figure 6.
Steady-state activation and inactivation characteristics of slow KA currents in bladder afferent neurons with TTX-resistant spikes from vehicle-treated and NGF-treated rats (2 weeks). A, Inactivation characteristics of slow KA currents in vehicle-treated animals (n = 15) (▴) and NGF-treated animals (n = 20) (▵). Relative peak amplitude of slow KA currents normalized to the maximal amplitude of slow KA currents (I/Imax) were plotted against membrane potentials. Vh and k obtained by fitting curves using the modified Boltzmann equation were −70.7 mV and −12.3 for vehicle-treated rats and −72.4 mV and −12.3 for NGF-treated rats. B, Activation characteristics of slow KA currents obtained in the neurons from vehicle-treated animals (n = 15) (■) and NGF-treated animals (n = 20) (□). Slow KA conductances normalized to the maximal slow KA conductance (G/Gmax) were plotted against membrane potentials. Vh and k obtained by fitting curves using the modified Boltzmann equation were −39.1 mV and 10.5 for vehicle-treated rats and −40.4 mV and 13.6 for NGF-treated rats. Error bars indicate SE.