Figure 7.
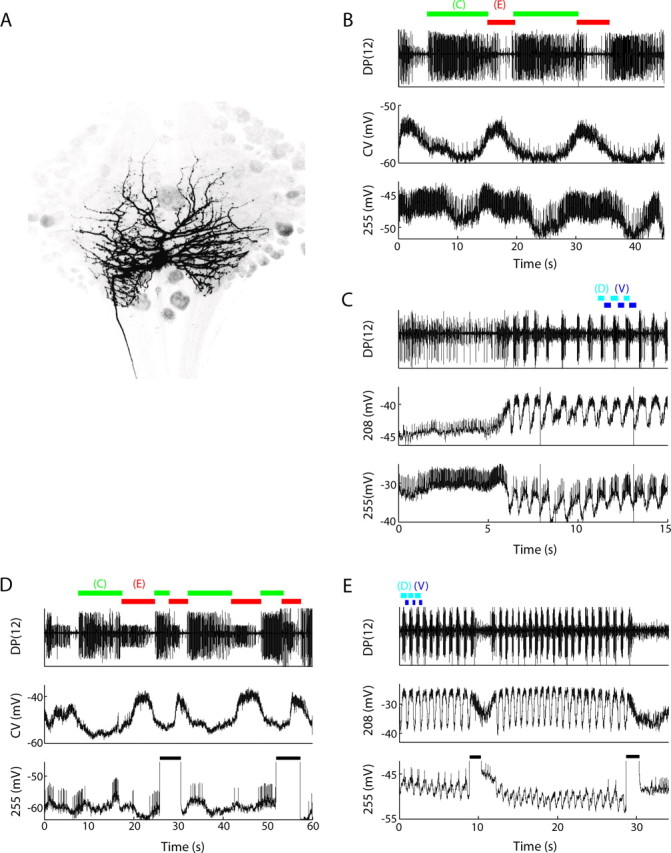
Cell 255 is a multifunctional interneuron. A, The morphology of cell 255, located in the posterior medial glial packet on the ventral surface. B, Dual intracellular recording of cell CV, a motor neuron to the ventral circular muscles, and cell 255, along with an extracellular recording of cell 3 spikes in the DP nerve. The DP recording was used to determine the timing of the contraction (C, green) and elongation (E, red) phases of the crawling motor program. Cell 255 oscillated in-phase with cell CV, depolarizing during the elongation phase of crawling. C, A dual intracellular recording of cell 208 and cell 255, along with a DP nerve recording to monitor the dorsal (D, cyan) and ventral (V, blue) phases of the swimming motor program. Cell 255 slightly led the oscillation of cell 208 and oscillated around a hyperpolarized potential below resting potential. D, Effects of depolarizing cell 255 on the crawling motor program. The recordings are the same as in B. Depolarizing current (+2 nA for 3–5 s; black horizontal bars) injected into cell 255 during the contraction phase of crawling terminated contraction and initiated elongation. The cell was held slightly hyperpolarized (−0.1 nA) during this trial. E, Effects of depolarizing cell 255 on the swimming motor program. The recordings are the same as in C. Depolarizing current (+2 nA for 1–2 s; black horizontal bars) injected into cell 255 terminated swimming.
