Figure 9.
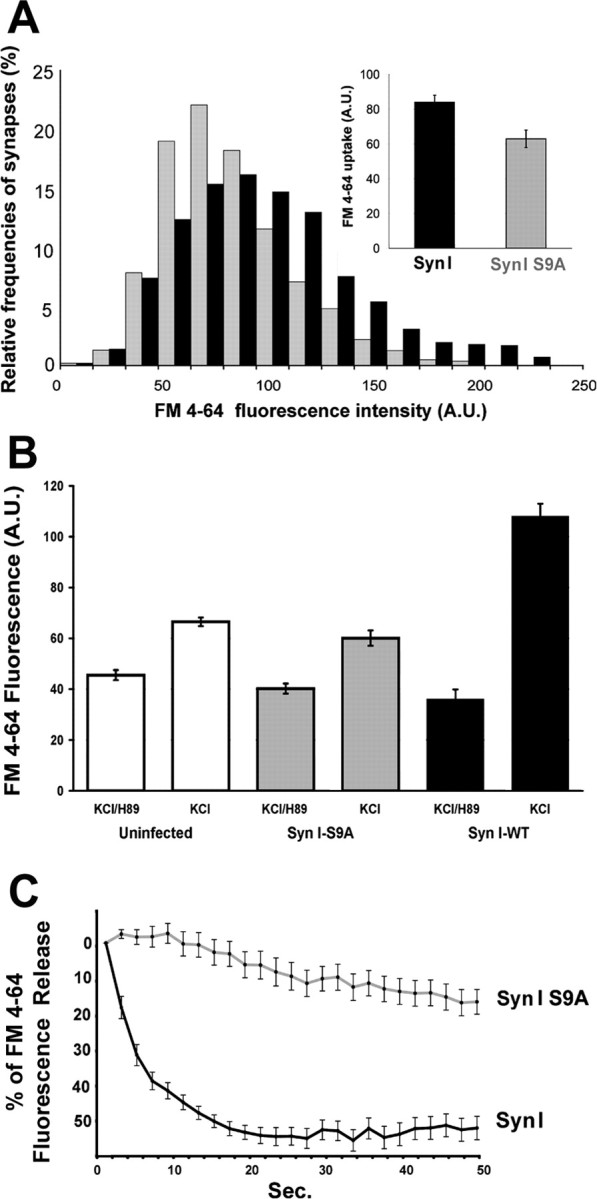
Expression of SynI S9A impairs SV exocytosis in synapsin I knock-out neurons. Hippocampal neurons in culture from synapsin I knock-out mice infected to express either ECFP–SynI or ECFP–SynI S9A under the PGK promoter were loaded with FM4-64 using a depolarizing stimulus for 1 min. A, Distribution of classes of FM4-64 fluorescence are shown in the histograms with the corresponding color coding. p < 0.001 for ECFP–SynI versus ECFP–SynI S9A, Bonferroni's multiple comparison test (n = 300 synapses from 3 independent experiments). Mean ± SE values of FM4-64 uptake (n = 3 independent experiments) are shown in the inset. B, Before the depolarizing pulse, neurons were incubated for 30 min with 10 μm H89. A second epoch of FM4-64 uptake was induced by applying the same depolarizing stimulus 30 min after the washing out of H89 and bleaching of the residual fluorescence. The increase in FM4-64 uptake after removal of the PKA inhibition is prominent in synapses expressing ECFP–SynI, whereas it is partially inhibited in synapses either uninfected or expressing ECFP–SynI S9A. p < 0.001 for neurons treated with H89 (either uninfected or infected with either vector) versus the same neurons after recovery from PKA inhibition and for neurons infected with ECFP–SynI versus either uninfected or ECFP–SynI S9A-infected neurons, after recovery from PKA inhibition; Bonferroni's multiple comparison test (n = 300 synapses from 2 independent experiments). C, The kinetics of FM4-64 destaining elicited from a second depolarizing pulse was evaluated by acquiring a stack of images at 2 s intervals and analyzing the progressive decrease in fluorescence at single synaptic boutons. Values have been corrected for bleaching and normalized. The average ± SE fluorescence intensities of 32 synaptic boutons per sample from three independent experiments are shown. A.U., Arbitrary units.
