Figure 4.
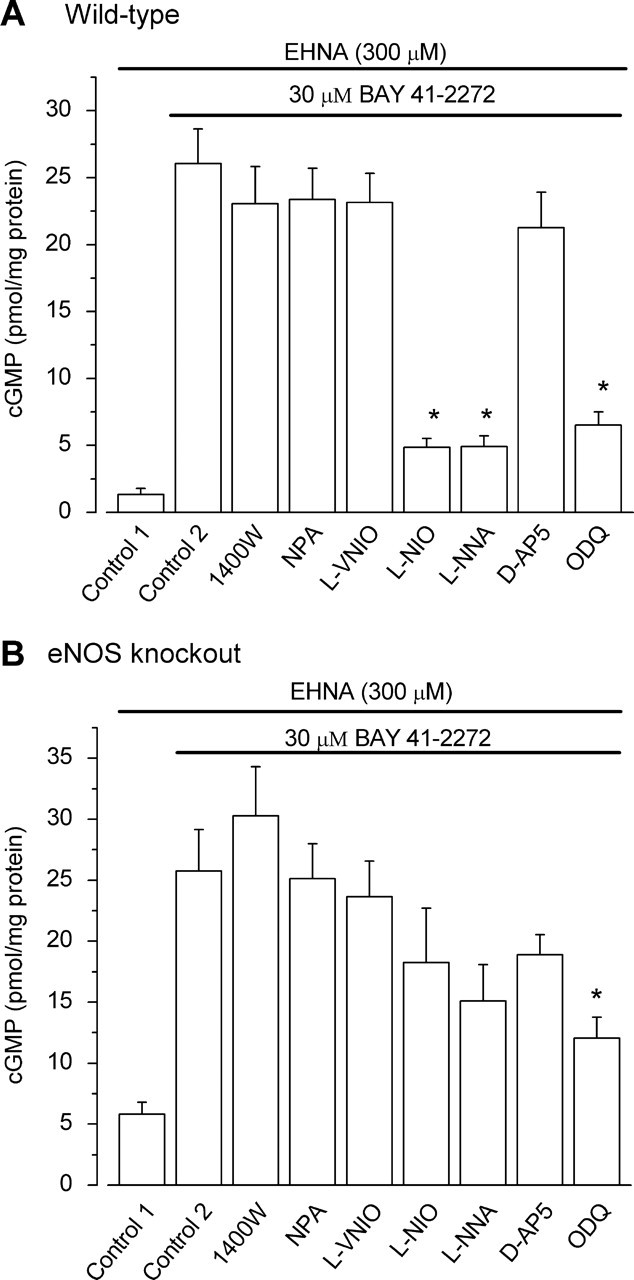
Tonic NO in wild-type and eNOS knock-out hippocampal slices. A, BAY 41–2272-stimulated cGMP accumulation in wild-type slices was unaffected (p = 0.97–0.98) by the nNOS/iNOS inhibitors 1400W (1 μm), NPA (1 μm), and l-VNIO (0.1 μm) or by 100 μm d-AP5 (p = 0.38) but was significantly reduced by l-NIO and l-NNA (both 100 μm), which are nonselective NO synthase inhibitors, or by ODQ (10 μm), an inhibitor of NO-activated guanylyl cyclase (*p < 0.001). B, At the same concentrations used in A, none of the NO synthase inhibitors significantly reduced BAY 41–2272-stimulated cGMP accumulation in slices from eNOS knock-out mice (p = 0.2–1). d-AP5 was also ineffective (p = 0.8), but the inhibition by ODQ was just significant. *p = 0.04; n = 15 in all cases. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA and Tukey's post hoc test.
