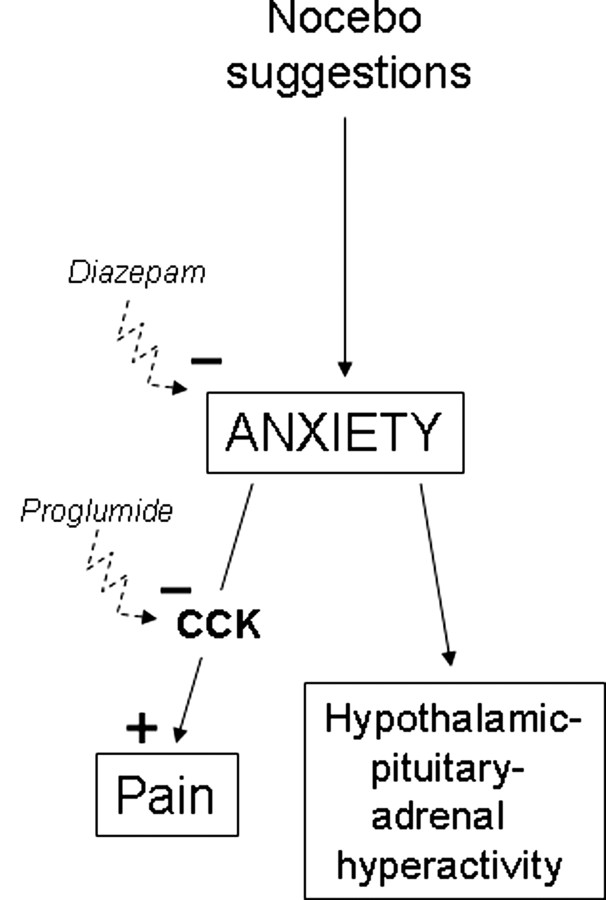
Figure 6.
Model to explain the findings of the present study. Nocebo-induced anxiety affects both the HPA axis and pain mechanisms. The link between anxiety and pain is represented by CCK, which has a facilitating effect on pain. Benzodiazepines, like diazepam, can block anxiety, thus preventing both HPA hyperactivity and hyperalgesia. CCK antagonists, such as proglumide, only block the CCKergic anxiety–pain link. Therefore, CCK antagonists do not inhibit pain per se but rather the anxiety–pain link.