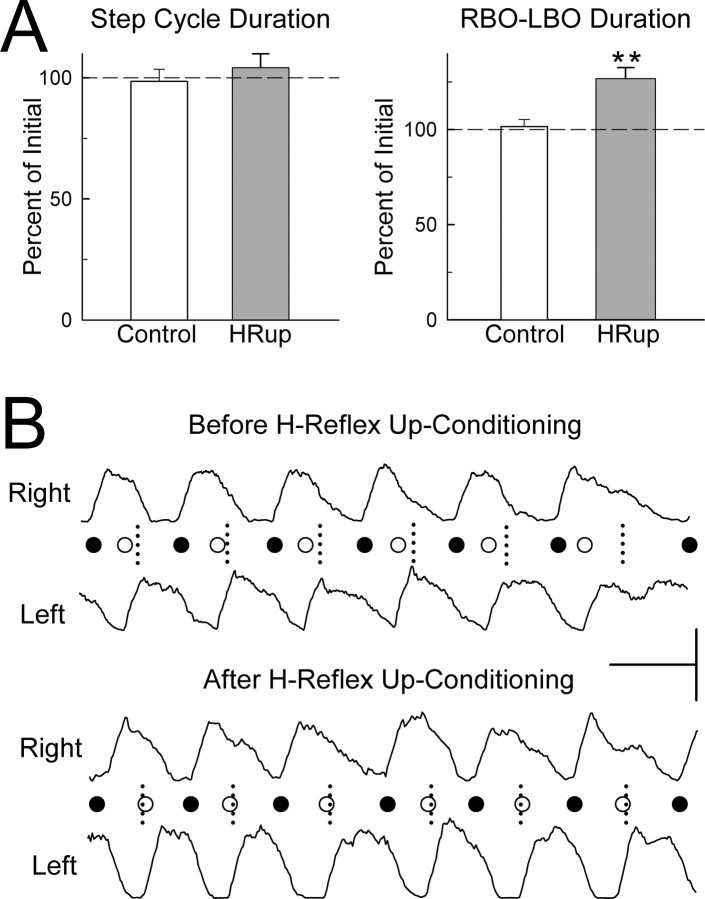
Figure 3.
Effects of H-reflex up-conditioning on the step-cycle. A, Average ± SEM step-cycle duration and RBO–LBO duration (time from right soleus burst onset to left soleus burst onset) for control rats (open bars) and HRup rats (solid bars) for the second treadmill session as percentage of their values for the first (i.e., initial) session. **p < 0.01, significant change from the first to the second session. Step-cycle duration is unchanged in both control and HRup rats. RBO–LBO duration (which was lower than normal in the first treadmill session; see Results) is increased in HRup rats only. B, Right and left soleus bursts (rectified EMG) from an HRup rat for the first (i.e., before up-conditioning) treadmill session and the second (i.e., after up-conditioning) session. Calibration: horizontal bar, 0.5 s; vertical bar, 100 and 150 μV for the right and left bursts, respectively. Each RBO (●) or LBO (○) is marked. The short vertical dashed lines mark the midpoints between RBOs (i.e., the midpoints of the step-cycles), which is the time when LBOs should occur (as in normal rats). Before H-reflex up-conditioning, LBO occurs too early; after up-conditioning, it occurs on time.