Figure 1.
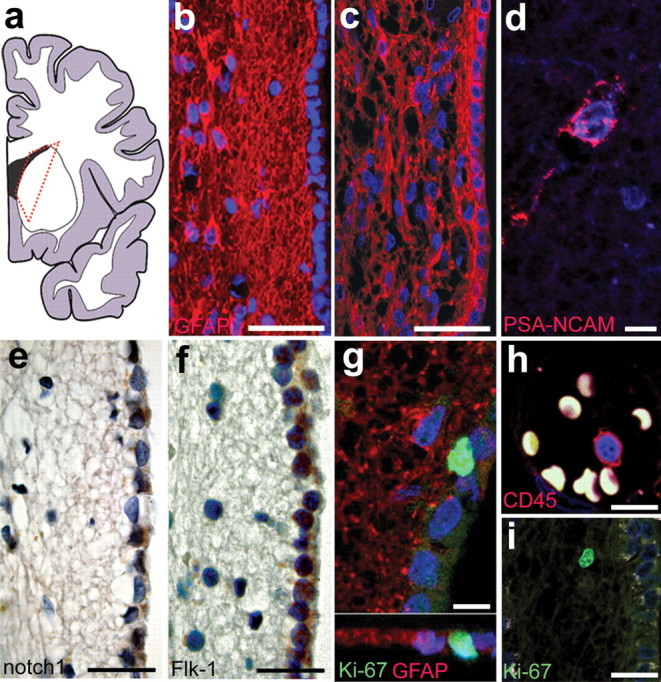
Cellular architecture and proliferative capacity of the adult human SVZ. a, Schematic overview of a human brain hemisphere with the dotted red line indicating the area of analysis. b, c, Representative histology of the SVZ with a gap between the ependymal layer and astrocytic ribbon in the medial part (b) and with the astrocytic ribbon being continuous from the ependymal layer to the brain parenchyma in the dorsal and ventral areas (c). d, Occasionally, PSA-NCAM-positive cells can be detected close to the ependyma or in the astrocytic ribbon and beyond. e, f, Molecules that were shown to regulate neurogenesis such as notch1 (e) and Flk-1/VEGFR-2 (f) are expressed in the ependymal cell layer. g, Proliferating Ki-67-positive cells are often closely associated with the ependymal layer. h, i, Lack of costaining with pan-hematopoietic markers such as CD45 (h) rules out a non-neural origin of the proliferating Ki-67-positive cells (i). Scale bars: b, c, 50 μm; d, g, h, 10 μm; e, f, 25 μm; i, 20 μm.
