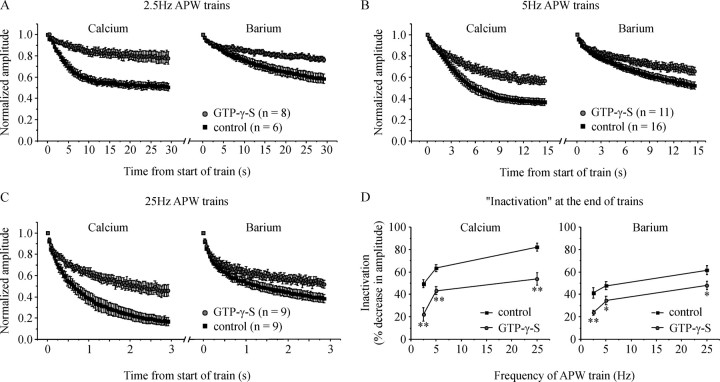
Figure 5.
G-proteins reduce inactivation of ICa over a range of stimulation frequencies. Cells were stimulated with a train of 75 APW first in Ca2+-containing extracellular solution and then in Ba2+-containing extracellular solution. A–C, Normalized current amplitude is plotted against time for cells stimulated at a frequency of: (A) 2.5 Hz, (B) 5 Hz (same data already shown in Fig. 2C), and (C) 25 Hz. D, Mean inactivation (percent decrease in current amplitude at the end of the APW train) is plotted against stimulation frequency for control cells and cells with GTP-γ-S in the patch pipette to activate endogenous G-proteins. GTP-γ-S significantly reduced inactivation at all three stimulation frequencies in both Ca2+-containing and Ba2+-containing extracellular solution (*p < 0.03; **p < 0.005). Error bars indicate SEM.