Figure 4.
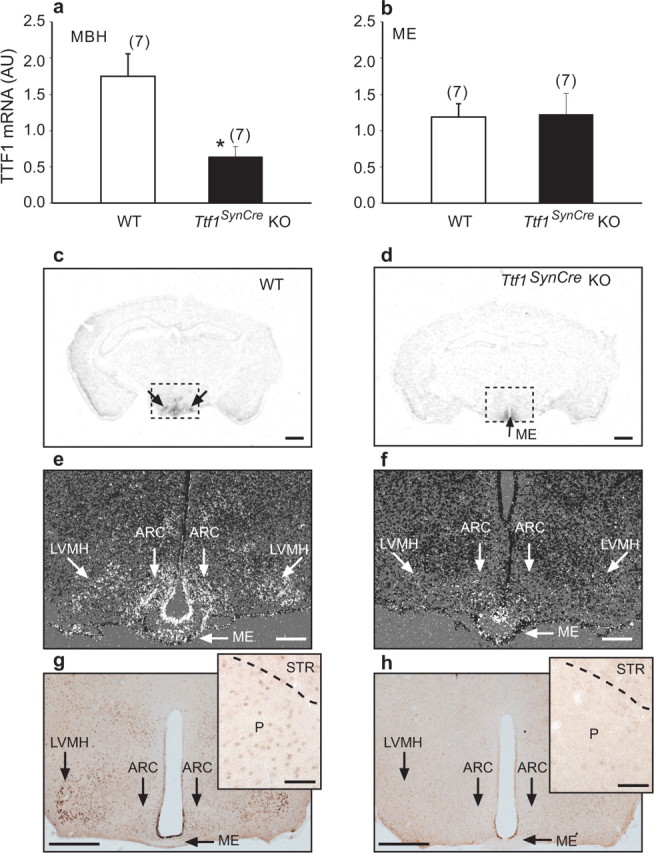
SynCre-mediated deletion of the Ttf1 gene reduces TTF1 expression in hypothalamic neurons but not ependymoglial cells, as assessed by real-time PCR (n = 7 per group), in situ hybridization (n = 3 per group), and immunohistochemistry (n = 3 per group) analysis of the brains from 60-d-old female mice. a, b, TTF1 mRNA content decreases in the MBH (a) but not in the ME (b) of Ttf1SynCre KO mice compared with WT animals, as assessed by real-time PCR. c, d, Coronal sections of the brain at the level of the MBH illustrating the presence of TTF1 mRNA in the MBH of WT mice (c; double arrows) and the loss of expression in the MBH but not the ME (d; single arrow) in Ttf1SynCre KO mice, as determined by in situ hybridization using a 35S-UTP-labeled TTF1 cRNA. e, f, Dark-field, higher-magnification in situ hybridization images showing the presence of TTF1 mRNA in specific MBH subregions including the arcuate (ARC), lateroventral medial nuclei (LVMH), and the ME of WT mice (e) and the selective loss of TTF1 mRNA in the same nuclei of Ttf1SynCre KO mice, without a change of expression in the ME (f). g, Detection of TTF1 protein in the LVMH, ARC, and ME of WT mice. Inset, TTF1 protein is also detected in cells of the pallidum (P), although at lower levels. h, Selective loss of the protein in the LVMH and ARC, with persistent expression in the ME of Ttf1SynCre KO mice, as determined by immunohistochemistry. Inset, Loss of TTF1 in the pallidum of Ttf1SynCre KO mice. STR, Striatum. Scale bars: c, d, 400 μm; e, f, 200 μm; g, h, 400 μm; insets, 50 μm. *p < 0.05 versus WT.
