Figure 1.
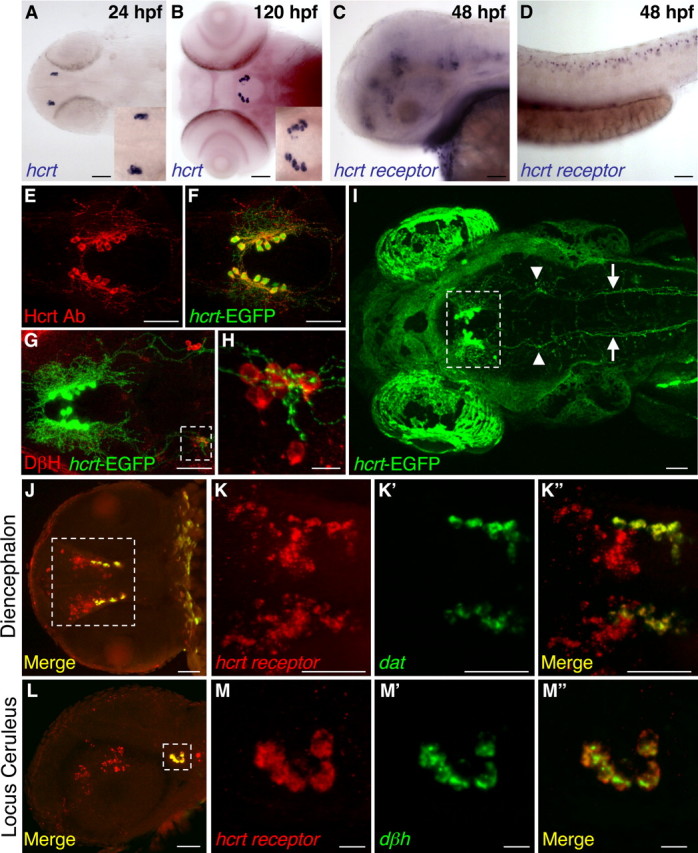
Hcrt and Hcrt receptor expression during embryonic and larval stages. A, B, hcrt mRNA is expressed in two bilaterally symmetric clusters of neurons in the posterior hypothalamus that each contains two to four neurons at 24 hpf (A, enlarged in inset) and 7–10 neurons at 120 hpf (B, enlarged in inset). At 48 hpf, hcrt receptor mRNA is expressed in discrete clusters of neurons in the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain (C) and in a row of neurons along the spinal cord (D). An Hcrt1 peptide-specific antibody (Ab) (E, F) and hcrt–EGFP transgenic fish (F–I) label Hcrt neurons and reveal extensive projections within the diencephalon (E, F, G, I), sparse projections to the forebrain (E, F), dense projections to the locus ceruleus [labeled with a dopamine β hydroxylase (DβH) antibody (G, H; arrowheads in I)], and projections down the spinal cord (arrows in I) at 120 hpf. EGFP-expressing Hcrt neurons are boxed in I to distinguish them from autofluorescence in the eyes and skin. The hcrt receptor is expressed in diencephalic dopaminergic neurons that express the dopamine transporter (dat) (J, K) and in noradrenergic neurons of the locus ceruleus that express dopamine β hydroxylase (dβh) (L, M). Boxed regions in G, J, and L are shown at higher magnification in H, K, and M. J is provided for orientation but was imaged from a different embryo than shown in K. Anterior is to the left. A, B, I–K are dorsal views, E–H are ventral views, and C, D, L, M are side views. Scale bars: A–G, I–L, 50 μm; H, M, 10 μm.
