Figure 4.
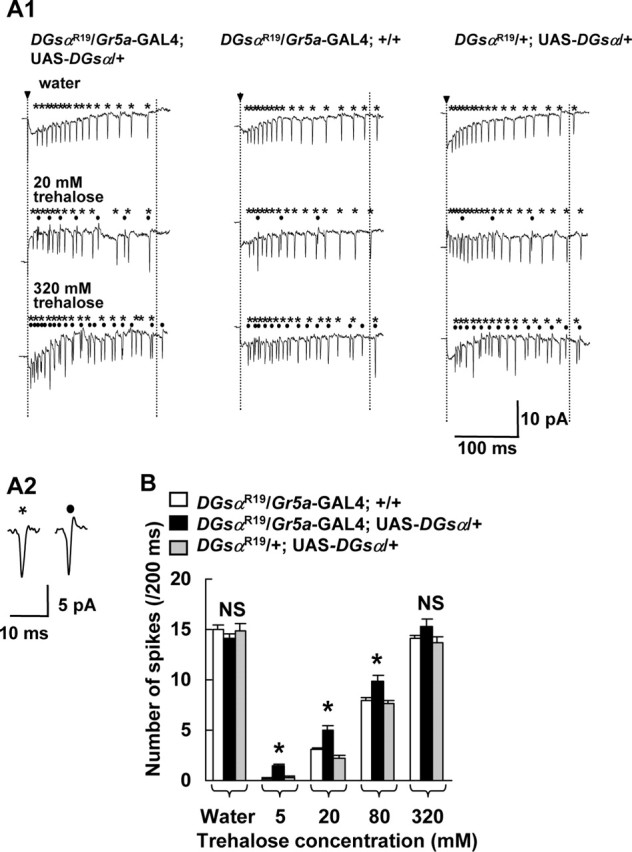
Electrical responses in GRNs to trehalose in heterozygous DGsα-null mutants. A1, Typical responses in L-type chemosensilla to water (7.5 mm KCl), 20 and 320 mm trehalose solutions in DGsαR19/+ flies carrying both Gr5a-GAL4 and UAS-DGsα (left three traces) and DGsαR19/+ carrying either Gr5a-GAL4 (middle three traces) or UAS-DGsα (right three traces) alone. Spikes marked with asterisks and dots were counted separately as a measure of magnitude of the response in a water-sensitive GRN (asterisks) and in a sugar-sensitive GRN (dots) during a 200 ms period starting from the onset of stimulus (period between two vertical dotted lines). Arrowheads indicate the onset of stimulation. A2, Two expanded traces represent typical spikes from a water-sensitive GRN (asterisk) and a sugar-sensitive GRN : B, Each column represents the number of spikes in a sugar-sensitive GRN during a 200 ms period starting from the onset of stimulus. A significant difference was found between DGsαR19/+ flies carrying both Gr5a-GAL4 and UAS-DGsα (filled columns) and DGsαR19/+ flies carrying either Gr5a-GAL4 (open columns) or UAS-DGsα (shaded columns) alone at 5, 20, and 80 mm trehalose (asterisks, p < 0.05). Columns marked “Water” represent the response to water of a water-sensitive GRN. Each column represents the mean ± SEM of 15 samples. NS, Not significant.
