Figure 7.
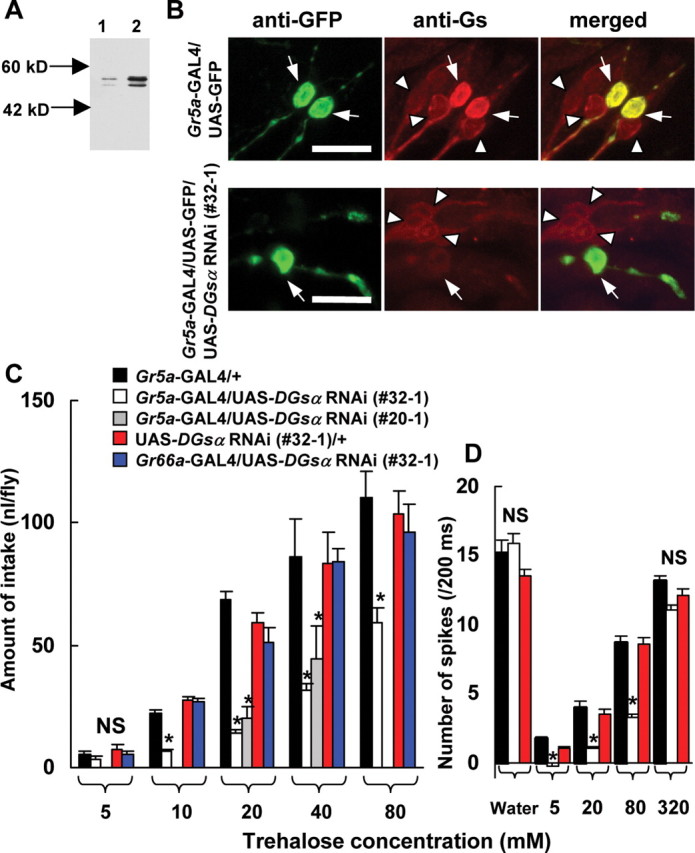
The effects of DGsα RNAi on immunoreactivities in larval CNS and GRNs (A, B) and on behavioral (C) and electrophysiological responses (D) to trehalose. A, Immunoblot of the DGsα protein obtained from larval CNS. Lane 1, DGsα RNAi expressed in larval CNS (1407-GAL4/UAS-DGsα RNAi). Lane 2, Control (+/UAS-DGsα RNAi). The antiserum recognized short and long forms of DGsα (Quan and Forte, 1990). B, Effects of DGsα RNAi expressed in Gr5a-GRNs. Control images stained with anti-GFP antibody (top left panel) and with anti-Gsα peptide antiserum (top middle panel), and merged (top right panel) in a transgenic fly expressing GFP in Gr5a-GRNs. The bottom panels are corresponding images in a transgenic fly expressing GFP and DGsα RNAi in Gr5a-GRNs. Arrows indicate Gr5a-GRNs. In the top panels, two Gr5a-GRNs (arrows) show immunofluorescence against GFP (left panel) as well as against Gsα (middle panel) resulting in yellow (right panel). In the bottom panels, in which DGsα RNAi was expressed, anti-Gsα fluorescence was very dim in a Gr5a-GRN (arrow in middle panel), resulting in green in a merged image (arrow in right panel). Immunoreactivities against Gsα in non-Gr5a GRNs (arrowheads) of both transgenic flies are visible. Scale bars, 10 μm. C, The amount of trehalose intake in DGsα RNAi-expressing flies [Gr5a-GAL4/UAS-DGsα RNAi (#32–1), open columns] was lower than in controls (black and red columns) at 10, 20, 40, and 80 mm trehalose (asterisks, p < 0.05). The amount of trehalose intake in another DGsα RNAi-expressing strain [Gr5a-GAL4/UAS-DGsα RNAi (#20–1), gray columns] was also lower than in control at 20 and 40 mm (asterisks, p < 0.05). Each column represents the mean ± SEM of 10 experiments. No significant difference was found among flies expressing DGsα RNAi in bitter-sensitive GRNs (Gr66a-GAL4/UAS-DGsα RNAi, blue columns) and controls (black and red columns). D, Electrical responses to trehalose in flies expressing DGsα RNAi (Gr5a-GAL4/UAS-DGsα RNAi). x- and y-axes are the same as Figure 4B. A significant difference was found among flies expressing DGsα RNAi [Gr5a-GAL4/UAS-DGsα RNAi (#32–1), open columns] and controls (black and red columns) at 5, 20, and 80 mm trehalose (asterisks, p < 0.05). Each column represents the mean ± SEM of 15 samples.
