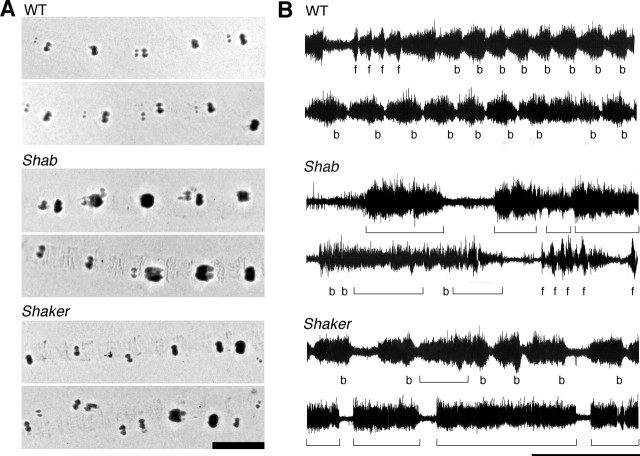
Figure 1.
Abnormal larval locomotion and central motor patterns in Shab and Sh. A, Mouthhook prints left on agar plates by locomotor activity of third instar larvae. WT larvae marked regular patterns during forward locomotion but Shab and Sh left irregular patterns with deep and shallow mouthhook prints. Scale bar, 1 mm. Numbers of larvae were 9–15 for each genotype. B, Burst firing of segmental nerves associated with propagating waves of muscle contraction in the semi-intact larval preparation, in which the CNS and segmental nerves were kept intact. WT displayed periodic bursts of spike activities coupled with posterior-anterior (b) or anterior-posterior (f) muscular contraction waves, resembling the peristaltic movement of intact larvae. In Shab and Sh, the nerve firing was often unassociated with the muscular contraction waves (brackets) and also lost rhythmicity. Scale bar, 1 min. The number of larvae was 6–7 for each genotype.