Figure 7.
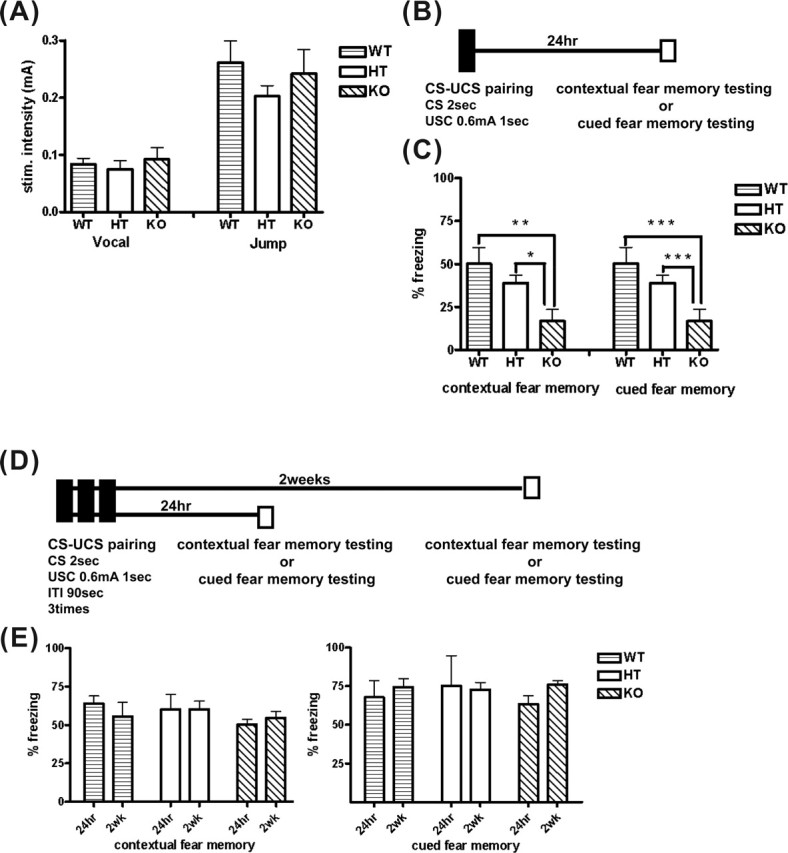
Consolidation of contextual and cued fear memory was impaired in the HPC-1/syntaxin 1A KO mice. A, Pain threshold to electrical footshock. Mice were exposed to a 2 s electrical footshock. The minimal intensity of a shock generating vocalizing or jumping response was determined. There were no significant differences among genotypes (WT, n = 5; HT, n = 5; KO, n = 5). B, Schematic showing a single CS–UCS pairing protocol. Each mouse received only a CS–UCS pairing in a conditioning chamber. Approximately 24 h after pairing, contextual fear memory testing and cued fear memory testing was conducted. C, Consolidation of contextual and cued fear memory by this training protocol was significantly impaired in KO mice compared with WT and HT mice (WT, n = 6; HT, n = 6; KO, n = 6). *p < 0.01; **p < 0.05. D, Schematic showing the overtraining protocol. Each mouse received CS–UCS pairings three times in a conditioning chamber. One day or 2 weeks after pairing, contextual fear memory testing or cued fear memory testing was conducted. E, Contextual (left) and cued fear (right) memory 24 h or 2 weeks after a CS–UCS pairing in KO mice was not significantly different compared with WT and HT mice (WT, n = 8; HT, n = 8; KO, n = 10). Data represent the mean ± SD.
