Figure 3.
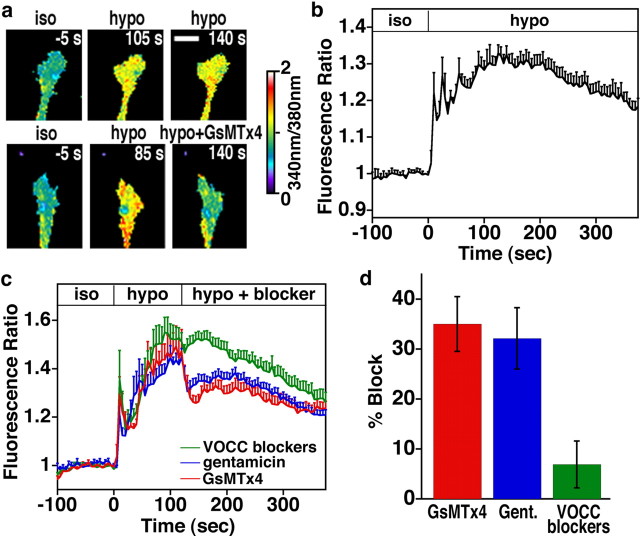
Ca2+ influx through SACs on Xenopus spinal neurons is activated by membrane stretch with hypotonic solution and inhibited with SAC blockers. a, Pseudocolored fluorescence ratio images of fura-2-loaded growth cones exposed to osmotic stretch with hypotonic solution. Growth cones were shifted from isotonic (iso) to hypotonic (hypo) solution at 0 s. In bottom row, after 120 s in hypotonic solution, SACs were blocked with 5 μm GsMTx4. Scale bar, 10 μm. b, Average fura-2 fluorescence ratio over time measured within growth cones exposed to a 46% hypotonic solution. Ca2+ transients followed by tonic Ca2+ elevations were typically observed. c, Average fura-2 fluorescence ratio over time measured within growth cones exposed to a 46% hypotonic solution followed by Ca2+ channel blockers [5 μm GsMTx4, 200 μm gentamycin, or a mixture of VOCC blockers (1 μm ω-conotoxin, 100 nm nifedipine, 50 μm NiCl, and 60 nm ω-agatoxin)] during the tonic phase. Data in b and c were normalized to the fluorescence ratio in isotonic solution immediately before addition of hypotonic solution. d, The average reduction in fura-2 fluorescence ratio (percentage of pretreatment) caused by each blocking condition measured at the point of maximum inhibition 5–25 s after application of each blocker. Only growth cones that exhibited a significant increase in Ca2+ (≥10% over baseline) after addition of hypotonic solution were included in this analysis. n ≥ 21 for all conditions. Gent, Gentamicin.