Figure 5.
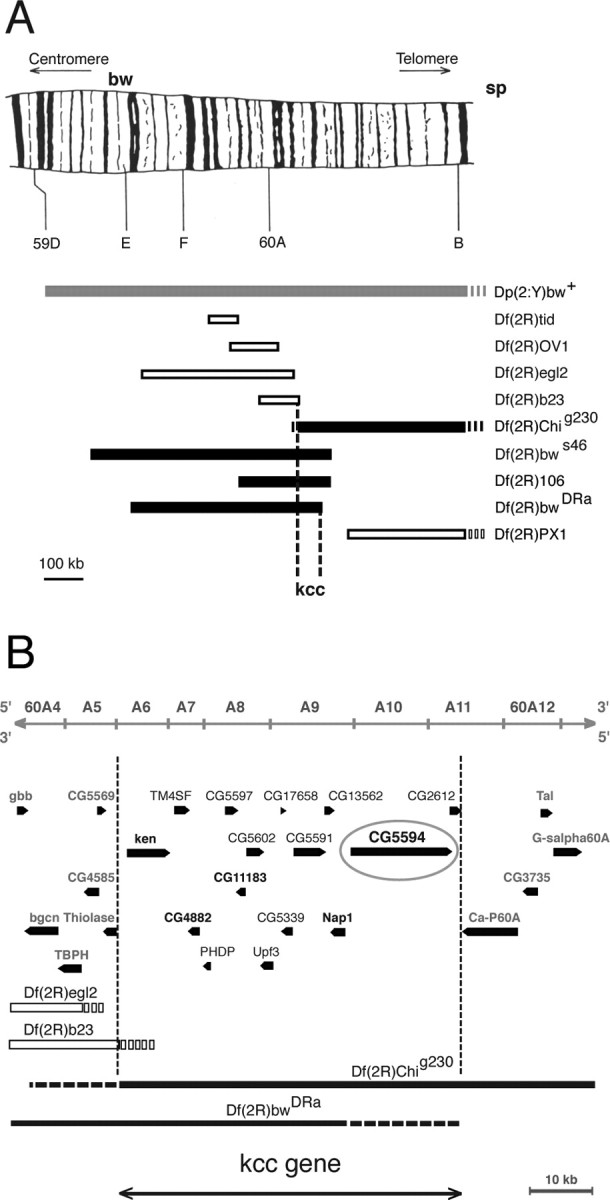
Genetic mapping of the kazachoc (kcc) gene. A, Initial recombination mapping experiments revealed that the kazachoc gene is located between the markers bw and sp on the distal tip of chromosome 2R. Subsequent duplication and deficiency mapping confirmed this result and further narrowed down the location of the kcc gene to a small cytological region (60A). A duplication of genomic DNA containing this region onto the Y chromosome (Dp(2;Y)bw+; 58F1-3; 60E11-12) produced a significant reduction in the bang sensitivity of homozygous kccDHS1 flies, indicating the presence of the kcc gene on the duplicated segment (gray box). Four of the deficiencies examined failed to complement kccDHS1 and therefore included the kcc gene (black boxes) (Df(2R)bwS46, Df(2R)Chig230, Df(2R)106, and Df(2R)Dra), whereas five others fully complemented kccDHS1 and therefore lacked the kcc gene (open boxes) (Df(2R)tid, Df(2R)OV1, Df(2R)egl2, Df(2R)b23, and Df(2R)PX1). The schematic drawing of chromosomal region 59D–60A has been reproduced with permission from Kurzik-Dumke et al. (1992). B, Superposition of the results of our deficiency mapping experiments onto a molecular map of the 60A cytological region (from Flybase) is shown. Deficiencies that uncover kcc are depicted as black boxes, and those that do not uncover kcc are depicted as white boxes; regions of uncertainty are shown as broken lines. The location of the kcc gene is bounded by the distal break points of Df(2R)b23, which does not uncover kcc, and those of Df(2R)bwDRa, which uncovers kcc. Hence, the kcc gene maps to a 57 kb region of 60A, which carries 15 genes. The distal break points shown for Df(2R)egl2 and Df(2R)b23, as well as the proximal break point for Df(2R)Chig230, are from Wharton et al. (1999). The position of the distal Df(2R)bwDRa break point takes into account the observations that this deficiency fails to uncover Ca-P60A (Periz and Fortini, 1999) but does uncover lethal mutations in CG4882, Nap1, or CG5594 (data not shown).
