Figure 8.
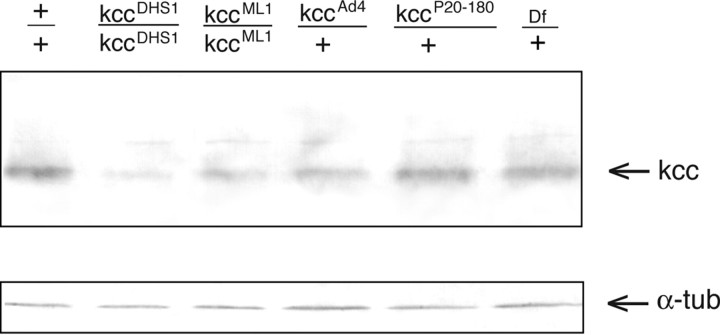
The kcc protein level is reduced in heads of kcc mutants. Shown is a Western blot of protein homogenates from the heads of wild-type (+/+) flies and various kcc mutants. The positions of both kcc and α-tubulin (α-tub) control bands are indicated by arrows. All of the strains produce an ∼125 kDa kcc protein. However, the heads of flies homozygous for the seizure-sensitive kccDHS1 mutation show a significant (∼4-fold) reduction in kcc protein. The heads of flies homozygous for the weaker kccML1 mutation also display a more modest (∼1.9-fold) reduction in kcc level. Flies heterozygous for the strong, lethal kccAd4 mutation show a threefold reduction in the level of kcc protein; those heterozygous for kccP20–180 show a more modest (1.6-fold) reduction in kcc protein. Flies carrying one copy of Df(2R)106, which removes the kcc gene, and one wild-type kcc allele (lane 6) display the expected twofold reduction in kcc level, suggesting that the protein levels used for quantitation are within the linear range.