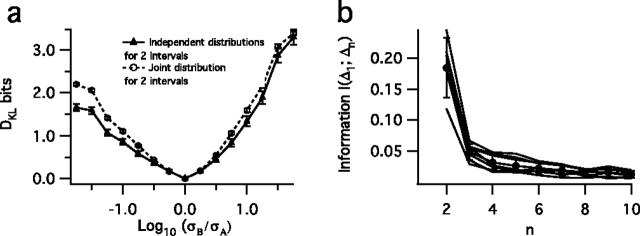
Figure 7.
Testing the independence assumption. a, Kullback–Leibler divergences calculated by using independent distributions for P(Δ1|σ) and P(Δ2|σ) (triangles) and joint distributions P(Δ1,Δ2|σ) (circles) as a function of the log ratio of two stimulus SDs, σB and σA, for independent distributions; error bars represent the SD. b, Mutual information, Equation 5, between the first spike interval and the nth interval of fly data for interval sequences that result from steady-state zero-mean stimuli with varying SDs. The sharp decrease between n = 2 and n = 3 suggests that dependence between intervals is confined mainly to the first and second interval; other intervals effectively are drawn randomly from the probability distribution. This information calculation was corrected for undersampling, as described in Materials and Methods. Gray lines represent the mutual information between intervals from different variance distributions, whereas the black line represents the mean; error bars represent the SD across different stimulus conditions.