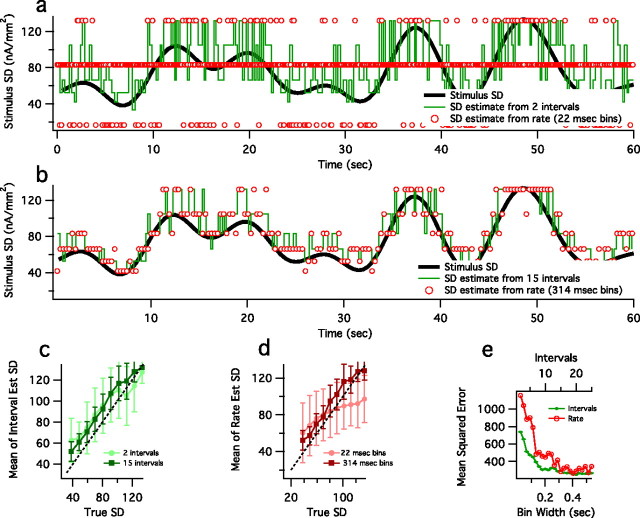
Figure 8.
Decoding a time-varying stimulus SD from HH spike trains by using 2 ISIs (a) and 15 ISIs (b, green lines). For each data point we find σ, for which P(Δn|σ) is maximized for either 2 or 15 intervals, as in Equation 6. Stimulus SD is estimated from the rate calculated in a window width equal to the mean time of 2 or 15 intervals (22 and 314 ms, respectively; red circles). The instantaneous stimulus SD is shown in black. At very short times, the range of possible estimates is limited when calculated from rate, but not from intervals. For longer times, the estimates from rate and intervals are comparable, because the HH model does not show slow spike frequency and would not be expected to display the ambiguity between rate and intervals as in fly neuron (Fig. 1). Shown is a comparison of estimated versus true SD, using intervals (c) and spike rate (d), in which the vertical bars represent the SDs of the estimated SD, and mean-squared error of the estimated SD (e) as a function of interval number or spike rate bin width.