Figure 2.
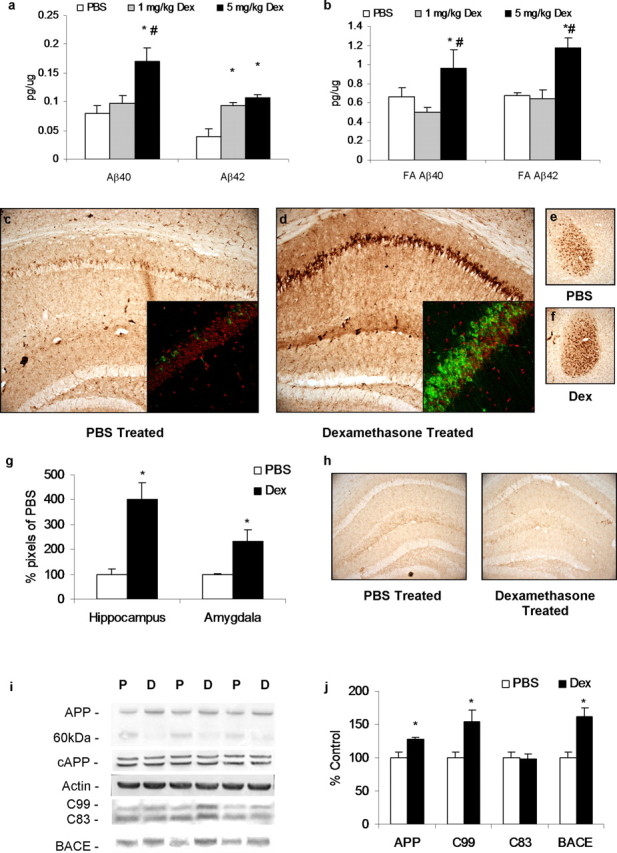
Dexamethasone treatment increases Aβ, C99, and BACE in the 3×Tg-AD mouse model. Four-month-old male 3×Tg-AD mice were treated daily for 7 d with 1 mg/kg (n = 5) or 5 mg/kg (n = 8) dexamethasone (Dex) or PBS vehicle (n = 8). a, Detergent-soluble Aβ levels were measured in whole-brain homogenates. Mice treated with 5 mg/kg dexamethasone (7 d; black bars) had significantly higher levels of Aβ40 and Aβ42 than vehicle-treated (PBS, 7 d; white bars) mice, whereas mice treated with 1 mg/kg dexamethasone (7 d; gray bars) had elevated Aβ42 compared with PBS controls. *p < 0.05, significance versus PBS controls for either Aβ40 or Aβ42; #p < 0.05, significance versus 1 mg/kg dexamethasone treatment. b, Detergent-insoluble Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels were significantly increased between 5 mg/kg dexamethasone treated and vehicle treated. c, e, DAB staining with 6E10 shows Aβ-like immunoreactivity in 40 μm sections from vehicle-treated mice. Hippocampus and amygdala regions are shown at 10× magnification. Inset demonstrates 40× confocal images with Aβ-like immunoreactivity shown in green and nuclear stain TOTO red shown in red. d, f, Same staining but in dexamethasone-treated animals. Aβ-like immunoreactivity was elevated in cell bodies of the hippocampus, as also shown by confocal imaging. g, Quantification of 6E10 DAB immunoreactivity in hippocampal and amygdala regions from PBS-treated and 5 mg/kg dexamethasone-treated groups. h, DAB staining with anti-CD45 shows that no activated microglia could be detected in the hippocampus of either PBS- or dexamethasone-treated animals. i, Western blot analyses of protein extracts from whole-brain homogenates of dexamethasone- and vehicle-treated 3×Tg-AD mice, shown as alternating lanes: P, PBS vehicle; D, 5 mg/kg dexamethasone treated. j, Quantification of protein blots from i shown normalized to β-actin levels as a loading control. Steady-state levels of APP are increased in the dexamethasone-treated group (6E10), whereas a 60 kDa band is similarly decreased, suggesting alternative processing. cAPP levels are unaltered, whereas C99 levels are increased but C83 levels remain unchanged. Furthermore, steady-state levels of BACE protein are increased concomitant to C99 levels. *p < 0.05, significance versus PBS controls.
