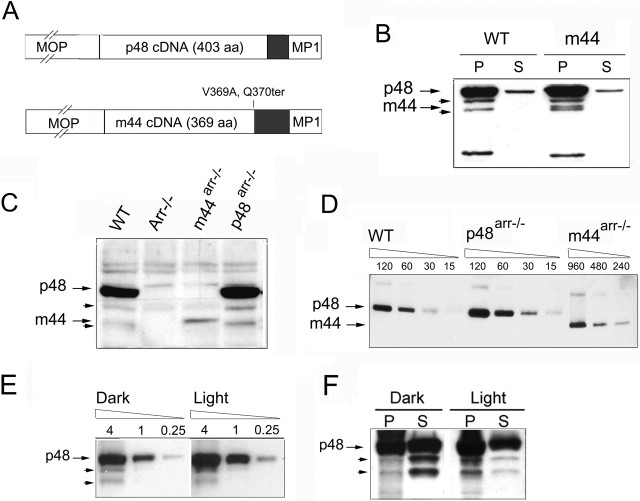
Figure 1.
Expression of the p48 or p44 forms of arrestin in transgenic mice. A, Expression vectors used for the generation of transgenic mice. The cDNAs encoding the p48 or m44 (murine Arr1–369,V369A,Q370ter) forms of arrestin were flanked by the murine rhodopsin promoter (MOP) and the mouse protamine 1 (MP1) polyadenylation signal. Gray boxes indicate 3′ end untranslated regions.B, m44 transgene expression in wild-type mice. Pellet (P) and supernatant (S) fractions of total retinal homogenates from light-adapted m44-positive and control mice were analyzed by Western blot using C10C10 antibody (specific for residues 290–297 of arrestin). The m44 protein in transgenic mice comigrated with p44 in bovine rod outer segment preparations (bROS), between two bands of ∼46 and 42 kDa (arrowheads), which are likely proteolyzed forms of arrestin. C, Expression of p48 and m44 transgenes in the Arr–/– background. Equivalent fractions of total retinal homogenates from the indicated mice were compared by Western blot. D, The relative abundance of arrestin isoforms in ROS from dark-adapted p48Arr–/–, m44Arr–/–, and wild-type mice determined by Western blot using C10C10 antibody. Numbers above each lane indicate total protein loaded in nanograms. Note that the range of dilutions loaded in the m44Arr–/– sample differed from those of the wild type and p48Arr–/–. E, Extent of p48 proteolysis was independent of lighting conditions. Retinal homogenates from dark- or light-adapted p48Arr–/– mice were subjected to serial dilutions and loaded in the same gel. Sample loaded (in micrograms of total protein) is indicated above each lane. The ratio of p48 to its proteolyzed forms is not affected by light conditions. F, Comparison of pellet and supernatant fractions of total retinal homogenates from dark- or light-adapted p48Arr–/– mice. The proteolyzed forms are enriched in the supernatant fraction of dark-adapted mice and the pellet fraction of light-exposed animals.